Endpoints are assets like laptops, IoT, or devices connected to an organization’s network. As the scale and complexity of these endpoints increase in an enterprise environment, security becomes paramount.
Researchers have found that 68% of organizations had experienced an endpoint attack that compromised their data or IT infrastructure. Managing these endpoints under standardized security policies is the key to maintaining a robust security posture.
Not only does endpoint security help you manage security at scale, but it also adapts to evolving threats that tend to trick traditional antivirus programs. In this article, we take a deep dive into understanding endpoint security and its components. This will help you choose the right solutions for your team, enabling you to update your security tech stack.
 What are Endpoint Protection Services?
What are Endpoint Protection Services?
An endpoint protection service is a software solution that is often provided by a third-party vendor to protect endpoint devices (any computing device that sends or receives communications over a network).
It is typically a managed offering that includes a range of security features to safeguard and monitor laptops, smartphones, servers, workstations, and IoT devices. It also extends protection to non-traditional assets like POS systems, appliances, cameras, and navigation systems.
Why Do We Need Endpoint Protection Services?
First off, it is common knowledge that your security is only as strong as your weakest link. This is true because attackers look for the path to the least resistance to exploit your organization’s IT assets. And with the increasingly distributed networks going live, the weakest link in the security chain is the endpoint.
So, it is no surprise then that 70% of cyberattacks start at the endpoint. Forrester surveys even found that about 15% of data breaches come from lost or compromised devices.
Some reasons why organizations now draft bigger budgets for endpoint security include but are not limited to:
- Safety and control of data: Data is a company’s most important asset these days. Losing it or even losing access to it could be enough to put the whole business at risk.
- Volume and complexity of endpoint devices: Companies are dealing with more endpoints and more types of them, which makes keeping them secure much harder.
- Hacker evolution: The threat landscape is getting smarter. Hackers are constantly finding new ways to break in, steal data, or trick employees into handing over sensitive information.
- More exposure: Remote work and BYOD policies make traditional perimeter security less effective, exposing more vulnerabilities.
- Cost implications and legal trouble: Companies must deal with the costs, shift resources away from other departments to handle threats, lose reputation after a security compromise, and pay fines for breaking compliance rules.
To handle these growing challenges, businesses must integrate a smart endpoint security service that connects all devices and fits into the bigger security setup, sharing threat info and helping respond to attacks automatically.
Real endpoint security is more than just antivirus software. It needs to use advanced tools to catch tricky threats. It should also give you 24/7 visibility and control, keeping everything in check, whether devices are on the network or not, ideally without needing a VPN.
Gartner MQ: Endpoint
See why SentinelOne has been named a Leader four years in a row in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Endpoint Protection Platforms.
Read Report
Key Features of Endpoint Protection Services
Endpoint protection services offer more than just protection from viruses and malware threats. IT security admins use these services to set up monitoring functions and data alt backups in case of an attack.
Some key features of these software solutions include:
1. Real-Time Endpoint Visibility
Losing endpoints like laptops or phones can be a huge security risk. With real-time visibility, you always know the geolocation of your computing devices.
If a device gets stolen, you can remotely wipe it before any sensitive data is leaked. Even better, you can collect info like its last location or trigger the device’s mic or camera to gather evidence.
2. Seamless Data Loss Prevention
It has become a staple in modern work environments for employees to use external drives or upload files to cloud networks when sharing or backing up data. While convenient, these channels can quickly become security risks and possibly cause accidental or malicious leaks.
Endpoint protection services offer DLP tools that monitor these activities in real-time, ensuring that sensitive data doesn’t leave the company’s control without proper authorization.
It works by analyzing data transfers, flagging risky behaviors (such as copying large amounts of sensitive data), and blocking unauthorized actions.
3. Adaptive Network Security Management
Endpoint services offer firewalls, ringfencing, and network control that work to build an adaptive setup that adjusts in real-time based on your devices’ activity.
It uses intelligent filtering to keep hackers and malicious traffic out while ensuring that legitimate business operations are not disrupted by overzealous security measures. This is especially handy if you have employees working remotely or moving around a lot.
4. Advanced Ransomware Protection
It monitors behaviors typical of ransomware, such as rapid file encryptions or unusual file access patterns, and responds by locking down the affected endpoint to prevent further damage.
5. Dynamic Application Control
You don’t want just any app running on your network, but it can be difficult to keep track of everything. Endpoint solutions offer application whitelisting that makes it simple by creating a smart list of trusted apps that can run.
The system continuously monitors new applications and updates, automatically adjusting permissions based on risk levels. This allows businesses to control the software environment without constantly updating manual lists.
Applications that don’t meet security standards or that behave suspiciously are blocked automatically.
6. Critical Data Access Management
Critical data access management provides a granular, role-based control system to ensure that only the right people have access to the most important information. With this, your business can enforce strict access policies on sensitive files and databases.
It works by using multi-factor authentication (MFA) and encryption, and even if an unauthorized person gains access, they can’t read or misuse the data.
7. Granular Access Elevation
This security measure grants admin rights or elevated privileges to users for specific tasks and then goes on to revoke those privileges immediately after. This reduces the chance of someone accidentally causing damage or an attacker exploiting admin privileges.
8. Built-in Integrations
Good endpoint security service software should easily communicate with other tools in your existing tech stack. Open APIs have to integrate smoothly with things like Active Directory, network monitoring, or intrusion prevention, making your security posture stronger as a whole.
Types of Endpoint Protection Services
Over the past couple of years, we have witnessed threat actors use more sophisticated and complex strains to exploit network systems, with a large part being ransomware operations.
Regardless of these dangers, a Fortinet survey reported that while 78% of enterprises claimed they were well prepared for an attack, about half still fell victim to cyber threats.
Understanding these challenges, here are types of endpoint protection services that can help with mitigation
1. Cloud-Based Endpoint Protection
Cloud is the biggest real estate stake in almost every company. While the truth of this is easily perceived, the numbers state that 44% of traditional small businesses are using cloud infrastructure or hosting services. Also, 66% of small tech companies and 74% of enterprises have also adopted these services.
This service type allows admins at these companies to manage security policies, apply updates, and monitor threats without needing on-premise infrastructure. Solutions of this type often include automated patching, real-time threat intelligence, and scalable protection as the organization grows.
2. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
This service actively monitors and pinpoints compromised devices and reacts accordingly to remediate and mitigate any associated risks. It gathers data on processes, networking connections, and any user activity.
For example, fileless malware threats like Poweliks can evade antivirus software because it lodges and hide in the system’s memory. EDR uses behavioral detection and indicators of compromise (IoCs) to recognize activities like unusual command-line executions or registry changes.
Once a threat is detected, EDR can automatically isolate the endpoint, start containing the attack, and remediate it by rolling back any changes or deleting infected files.
3. Data Encryption
This service type focuses on securing your data both at rest and in transit by simply converting it to unreadable code, rendering the packets useless to unauthorized users/entries.
For cloud-based endpoints, end-to-end encryption (E2EE) ensures data is encrypted from the sender to the recipient, preventing man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
4. Antivirus and Anti-Malware Protection
Still the first line of reactionary measures against cyber threats, these services detect and remove malicious software, such as viruses, ransomware, spyware, and other forms of malware from endpoint devices.
AVs mostly use signature-based detection and heuristic analysis to catch threats and some other complex attack vectors like Trojan horses, worms, and rootkits.
5. Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention
Endpoint firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) put up a virtual barrier between a trusted and an untrusted/foreign network. It is the first proactive defense line and works by filtering network traffic to prevent attacks like port scanning or DoS (Denial of Service).
Basic firewalls use stateful packet inspection, but more advanced solutions integrate deep packet inspection, which examines data packets for suspicious content. Firewalls report malicious network IP addresses and prompt the system to automatically drop receiving packets.
6. Sandboxing
The goal is to make sure you curtail and contain safely any active threat to prevent escalation.
Sandboxes add another layer of endpoint security by providing an isolated environment where suspicious or unknown files, links, or code can be safely executed without impacting the rest of the network.
When a file or program is flagged as potentially dangerous (but hasn’t been conclusively identified as malware), it is sent to the sandbox environment where its behavior can be observed in real-time.
It allows the security system to see if the file tries to exploit vulnerabilities, modify system settings, or initiate connections to malicious servers.
Once inside the sandbox, if the file exhibits harmful behavior, it’s flagged as malware and automatically blocked or quarantined.
7. URL Filtering
This service controls the web traffic accessed on endpoint devices. It analyzes the URLs that users attempt to visit and compares them against a list of known harmful or blocked sites (such as phishing or malware-laden websites).
For instance, drive-by downloads—malware that installs automatically when a user visits a compromised site—can be blocked before they occur.
URL filtering helps businesses ensure employees stick to work-related sites by blocking access to non-productive or restricted ones.
It can also work with cloud-based DNS services to stop harmful websites before they even load by filtering out bad domain names. This keeps your devices and network safe from phishing sites and other malicious content without slowing things down.
Benefits of Endpoint Protection Services
The primary advantage of endpoint protection services is that all threats are detected across the expanse of your organization’s assets.
Below are a few more benefits of incorporating an endpoint protection security.
- Protects against diverse threats. Endpoint security solutions rely on behavior rather than signatures to identify threats. This allows them to catch zero-day exploits, which are nothing but unknown vulnerabilities.
- Improves network security. Consistent security policies applied across the network reduce the chances of endpoints succumbing to cyberattacks. Moreover, endpoint security solutions isolate the threat and limit its propagation through the network, preventing the lateral movement of threats.
- Offers threat detection and response in real-time. Endpoint security software uses AI-based detection techniques to spot anomalies. They give a real-time response, limiting the extent of damage while offering ways to roll back changes.
- Reduces attack surface. During consistent monitoring, the solutions look into assets and the systems users run. If an asset needs an update, the endpoint security tools work alongside vulnerability management software to help assess vulnerabilities and update assets with relevant patches.
- Centralizes visibility and management. Endpoint security platforms like Singularity™ Endpoint detect all endpoints connected to an organization’s network. They help businesses identify unsanctioned devices and implement the same policies across all organization assets.
Discover Unparalleled Endpoint Protection
See how AI-powered endpoint security from SentinelOne can help you prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats in real time.
Get a DemoBest Practices for Implementing Endpoint Protection Services
Ponemon 2022 risk management report has it that on average, an enterprise manages about 135,000 endpoints and about 48% (64,800) of these devices are at risk of compromise because they are flying under the radar due to outdated OS.
In the report, Bryan Seely, an infamous hacker, told Ponemon:
“There isn’t a target on earth that I’m aware of that can’t be taken by force of some kind. The more effort it requires to successfully breach a target, the less attention it will get from a hacker. I can promise you they are paying attention and are ready to act when they see the easy or convenient way, and by then, it will be too late to stop them.”
We think he’s very much right. As we have made clear earlier, endpoints are the weakest entry points for bad actors to gain access to your organization’s confidential information, hence the need to protect them.
Here are some recommended practices when employing endpoint protection services at your organization:
1. Track and Secure Every Device Across the Network
With so many remote workers and mobile devices in use, it’s easy for IT teams to lose sight of endpoints, and that’s where security gaps form.
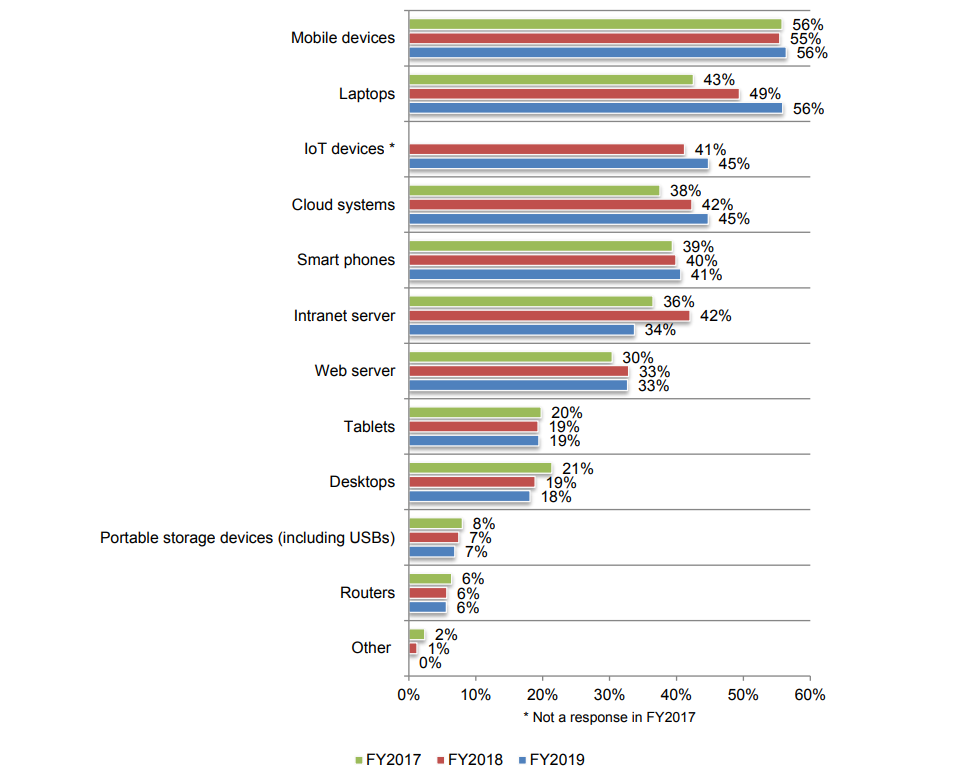
In fact, in 2019, 55% of professionals saw smartphones as the most vulnerable devices, and Zippia says about 75% of U.S. employees use personal devices for work.
By consistently monitoring all devices, you can build a network inventory or map that gives IT teams greater visibility and control. This simple step helps ensure nothing slips through the cracks, making it harder for threats to go unnoticed.
 2. Limit Access with Strict VPN Policies
2. Limit Access with Strict VPN Policies
A VPN encrypts internet traffic and hides your IP address, but not all VPNs are equally secure, and weak policies can still leave you exposed. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in VPNs to launch attacks like spoofing, sniffing, or even DDoS attacks.
By enforcing a strong VPN policy with multi-factor authentication (MFA), you make sure only verified endpoints can access your network remotely.
You can also take it a step further by banning or limiting VPN use and only allowing access at the application layer, which reduces the chances of a network-level attack.
3. Prevent Shadow IT
Shadow IT happens when people or departments use unauthorized software or devices without telling the IT team. These devices often are not secure and can pose a serious risk if they connect to your network. Attackers can exploit these unsecured endpoints to break into your system.
To keep your network safe, do regular assessments, every three months is a good rule of thumb to find and block any unauthorized devices.
Also, create a clear policy for employees about which tools and devices are allowed, and make sure they understand the risks of shadow IT.
4. Automate Updates and Patch Management to Close Security Gaps
Installing updates, patches, and software regularly is a must, but it’s something that often gets overlooked.
On average, it takes 97 days to apply patches, leaving devices exposed to security flaws. This delay can have real consequences.
Take the MOVEit breach on Caresource in June 2023, for example. The Clop ransomware group exploited a zero-day vulnerability before it applied the available patch.
Over 3.1 million individuals’ personal data, including Social Security numbers and health information, were exposed in this attack.
5. Use Encryption for All Remote Endpoints
Full-disk encryption protects everything on the device, while file-level encryption ensures data stays secure during transit or sharing. Both ensure that even if a device is lost or stolen, sensitive info stays unreadable to outsiders.
If you’re tight on budget or time, prioritize what you encrypt. Start with critical data like financial records, customer personal info, and confidential business documents. Then, gradually work your way through the rest of your data to keep everything locked down and secure over time.
6. Run Penetration Tests to Find Weak Spots
Running penetration tests (pen tests) regularly helps pinpoint weaknesses in your endpoint protection. These tests simulate real-world attacks, like trying to exploit known vulnerabilities (CVE) or weaknesses in configurations.
Pen tests often include methods like SQL injection (SQLi) or cross-site scripting (XSS) to see if hackers can get in.
By conducting black box testing (where testers don’t have inside knowledge of the system) or white box testing (where they do), you can find hidden security flaws. Running these tests regularly lets you close gaps before attackers can exploit them.
7. Segment Network to Limit Damage
This is a smart way to contain threats and stop them from spreading to your critical systems. To keep things manageable, start by setting up a highly privileged area for sensitive resources and then segmenting the network in smaller, controlled steps.
Keep in mind how different departments and teams communicate and work together when designing the segmentation. You don’t want to slow down workflows or create unnecessary obstacles for employees. For privileged resources, set up a separate infrastructure just for managing and updating those assets. Also, make sure the configuration systems for these privileged machines are completely isolated from those used for regular devices, keeping everything secure and streamlined.
8. Incident Response Planning to Minimize Impact
When building an incident response plan, it’s important to lay out clear roles, communication processes, and detailed steps to contain, eliminate, and recover from an attack. Being prepared helps businesses reduce downtime, protect data, and minimize overall damage.
To create an effective plan, follow these steps:
- Create a policy: Define who’s responsible for what, what tools and technologies to use, and how issues will be detected and addressed.
- Assemble your team: Include key roles like a CISO, a security manager, communication specialists, and IT security experts. Everyone should know their role, from technical tasks to communicating with the rest of the company or external stakeholders.
- Identify risks: Assess your endpoints to identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities.
- Analyze and prioritize: Investigate any security issues and rank them by risk severity so you know which threats to tackle first.
- Contain and eliminate: Act fast to contain the problem, isolate infected devices to prevent it from spreading, and then remove the malware or security risk entirely.
- Recover and restore: Get your endpoints back to working order as quickly as possible.
- Learn and document: After the incident, document everything that happened, from how the breach occurred to the steps taken to fix it. This helps you improve the plan and avoid similar incidents in the future.
Endpoint Protection with SentinelOne
SentinelOne offers EPP + EDR on a single agent without adding costs incurred by adding multiple agents. It offers AI detection that detects threats based on behavior while running checks before executing a file. It includes analyzing the characteristics of a file, such as if it is unknown or how it is packed if something looks suspicious.
Even if any machine gets infected, you can easily roll back to a previous instant using Ransomware Rollback Capability. It’s a patented technology you get from SentinelOne on Windows machines.
Beyond EPP and EDR, SentinelOne offers a range of functionalities to strengthen endpoint security, including:
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is a security approach that integrates multiple security products into one system. Its components expand visibility while providing more coverage to protect endpoints.
Solutions like Singularity XDR aggregate native endpoint, cloud, and identity telemetry with third-party security data, offering a broader security view. The XDR’s increased visibility gives analysts more context when dealing with security incidents. XDR becomes a platform for aggregating analytics and security data from all sources, making it easier to neutralize threats faster.
RemoteOps Forensics
RemoteOps forensics is a solution that provides the evidence required to investigate security incidents at a deeper level. It provides the insights you need to understand how a cyber attack happened.
This data is often viewed alongside EDR’s data to gather deeper analytics, giving more context to an incident response team to control the damage caused by the cyberattack.
Comparing forensics with EDR data often becomes tricky in chaotic times without automation. Singularity workflows automate this process, so insights are obtained rather than more data to analyze. It accelerates deeper investigation while streamlining a response in the event of a cyberattack targeting multiple endpoints.
Threat Intelligence
The threat intelligence component contextualizes security incidents by attributing them to specific threat actors or campaigns targeting your organization’s endpoints. It helps you put proactive defenses based on your threat hunting, led by intelligence.
Singularity threat intelligence allows you to prioritize security incidents in real-time, minimizing the potential impact while identifying adversaries in your environment.
Vulnerability Management
Studies reveal that 26% of breaches involve attackers exploiting a vulnerability. Surprisingly, 62% of organizations aren’t aware of such vulnerabilities in their environment, making them potential victims of a cyber attack.
The vulnerability management component of an enterprise security solution will ensure all endpoint systems are patched to the most up-to-date versions. SentinelOne’s Singularity vulnerability solution can detect at-risk assets and help enterprises evaluate their posture with continuous vulnerability assessment and management.
Learn more about ransomware rollback and understand how technology makes it easier to recover from such incidents.
Protect Your Endpoint
See how AI-powered endpoint security from SentinelOne can help you prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats in real time.
Get a DemoConclusion
Endpoint security implements security controls over the organization’s assets while moving above device-level protection. It safeguards devices connected to an enterprise network against known and unknown threats, giving you a well-rounded approach to cybersecurity.
Start incorporating endpoint security service software like Singularity to your security tech stack to strengthen your security posture against threats that target endpoints.
Learn more about SentinelOne’s Singularity Complete and understand how the platform keeps enterprise endpoints secure.
FAQs
Endpoint protection is a security measure focused on securing the devices (endpoints) connected to a network. It works by constantly monitoring these devices, spotting suspicious activity, and quickly responding to threats.
It also ensures security policies are followed and that devices are always up to date with the latest patches to close any gaps that hackers could exploit.
Traditional antivirus tools rely on scanning known malware signatures from a threat database to spot malicious software on individual devices. Endpoint protection services use behavior-based detection to catch suspicious activity, often analyzing patterns across the entire network of connected devices.
Unlike antivirus, which is mainly reactive, endpoint protection software is proactive and comes with EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) features to limit the damage if a threat slips through.
Endpoint protection services defend against a range of threats, including:
- Zero-day exploits targeting unpatched vulnerabilitiesMalware (viruses, worms, ransomware)
- Fileless attacks that exploit legitimate processes
- Ransomware that encrypts data
- Phishing attacks from malicious emails or sites
- Advanced persistent threats (APTs)
- Insider threats, both intentional and accidental
Yes, endpoint protection services can help with ransomware. They often come with features like blocking dangerous websites, emails, or downloads that might carry ransomware.
Tools like URL filtering, email scanning, and app control help stop users from accidentally triggering ransomware. Plus, some services work with backup solutions, so if files get encrypted, you can recover them without paying the ransom.

