GhostLocker RaaS: In-Depth Analysis, Detection, and Mitigation
What Is GhostLocker RaaS?
GhostLocker RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service) emerged in late 2023 and is associated with GhostSec, a Gaza-related hacktivist group. The group is loosely associated with other collectives such as SiegedSec, ThreatSec, Stormous, and the now defunct BlackForums. Collectively these entities have been referred to as The Five Families.
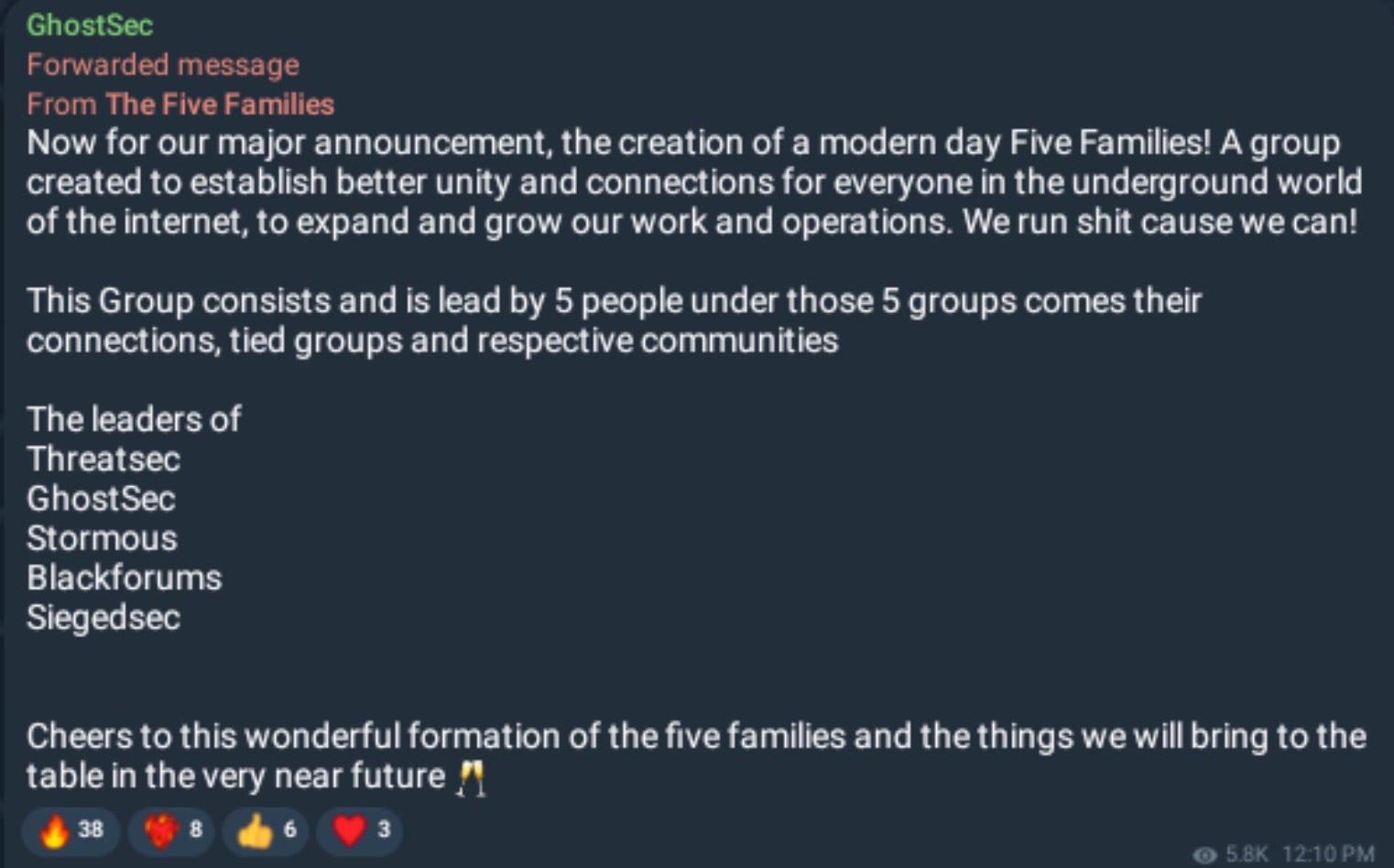
GhostLocker RaaS is primarily promoted and advertised across GhostSec’s Telegram channels as well as their linked communities. Actors behind GhostLocker are also associated with GhostStealer.

What Does GhostLocker RaaS Target?
GhostLocker is a public RaaS, aligned with the hacktivist group known as GhostSec. Affiliate targeting will vary, however, and GhostLocker campaigns to date have been aligned with the political ideologies of GhostSec, including those from Canada, Israel, Lebanon, Sudan, and Brazil.

How Does GhostLocker RaaS Work?
GhostLocker RaaS offers affiliates a web-based builder and management portal. The builder portal allows for customization of the ransom amount, campaign details, and technical behavior of the generated ransomware payloads. This includes control over what processes or services are terminated, what paths or locations are encrypted, whether or not to disable inhibiting services along with additional anti-detect features like execution delay, self deletion, persistence, and more.
GhostLocker payload uses Fernet (symmetric encryption) for full file encryption. Fernet is sometimes referred to as a basic “secret key” implementation. Initial (v1) releases of GhostLocker were heavily advertised on Telegram.
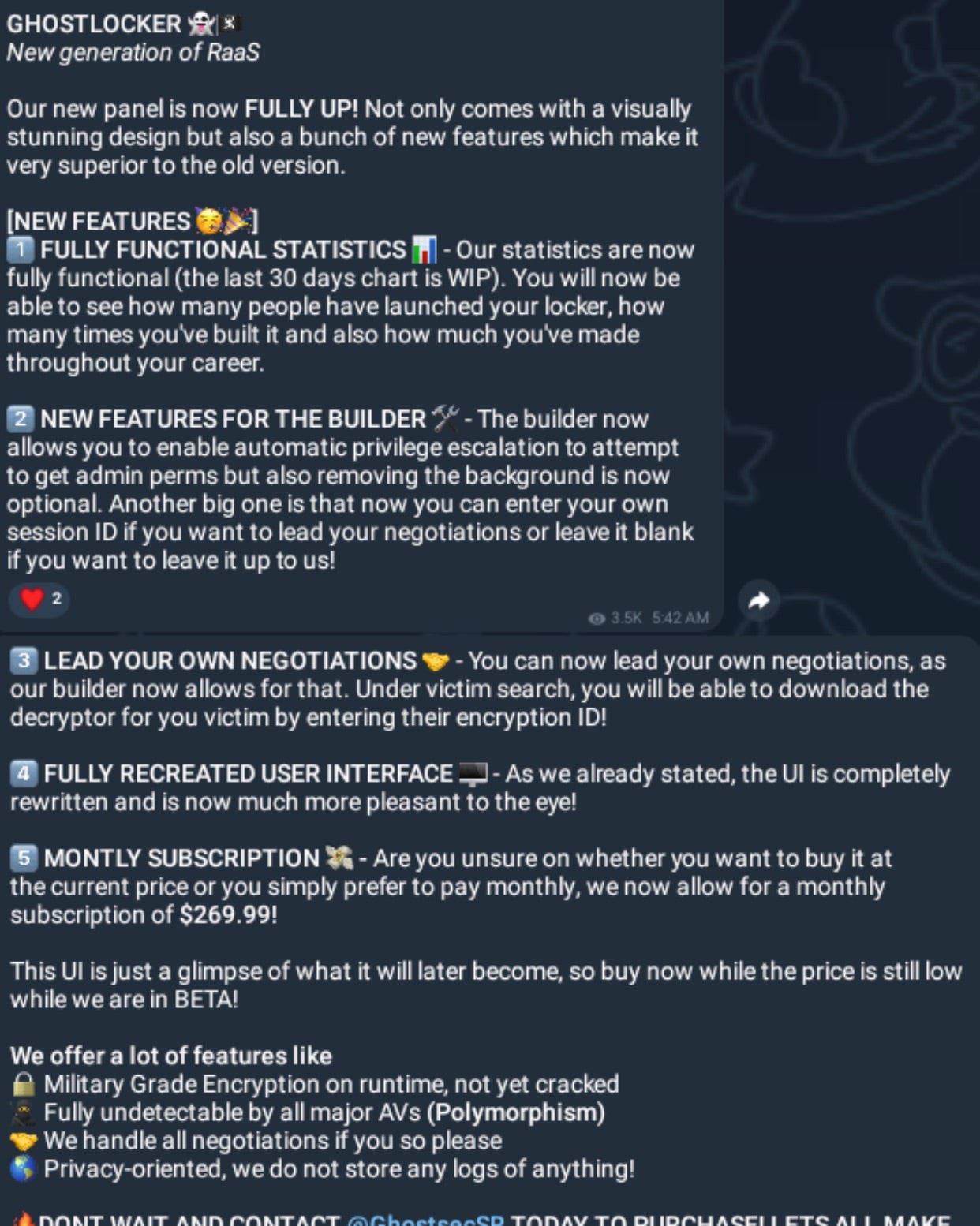
GhostLocker RaaS is currently being offered to affiliates for between $999 and $1,200 USD. The group also offers referral discounts to affiliates that recruit other members to the RaaS. These discounts are, historically, $200 USD off the initial fee, plus 5% of the newly recruited members attack revenue, resulting in a pseudo-RaaS pyramid scheme-type structure.
Upon encryption, affected files are modified with the .ghost extension. GhostLocker ransom notes are written to the desktop folder of victim devices and opened upon termination of the malware payload.
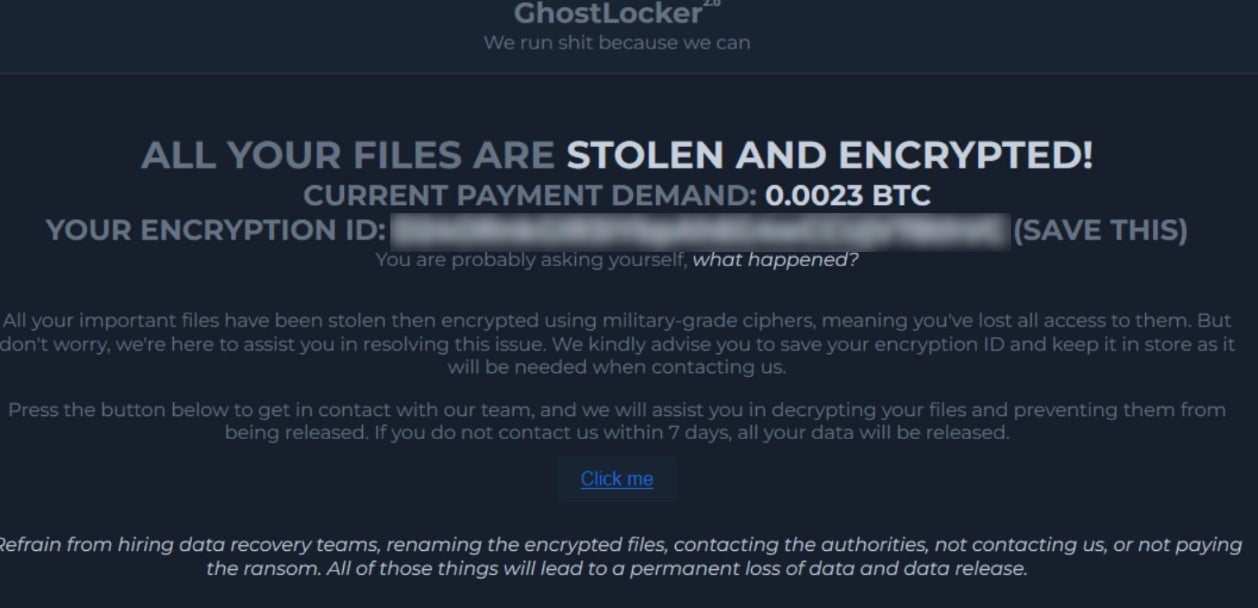
Payloads for GhostLocker consist of compiled Python code; multiple python scripts wrapped into executable file form.
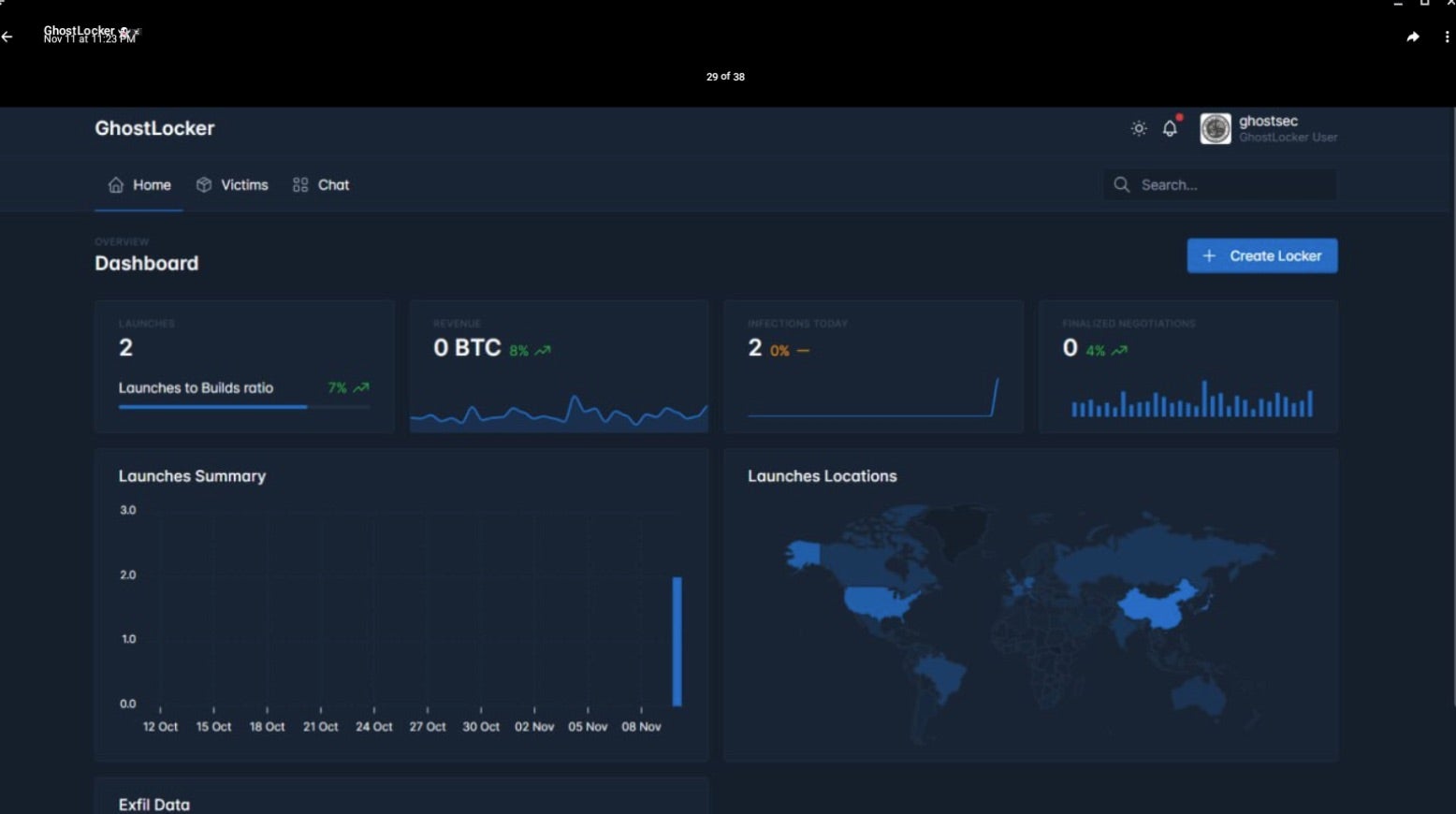
In January of 2024, the updated “REWRITE” (aka 2.x) version of GhostLocker was released and heavily promoted. Current versions of GhostLocker are written in Golang and affiliates are offered a fully featured management panel for tracking campaigns and payouts.
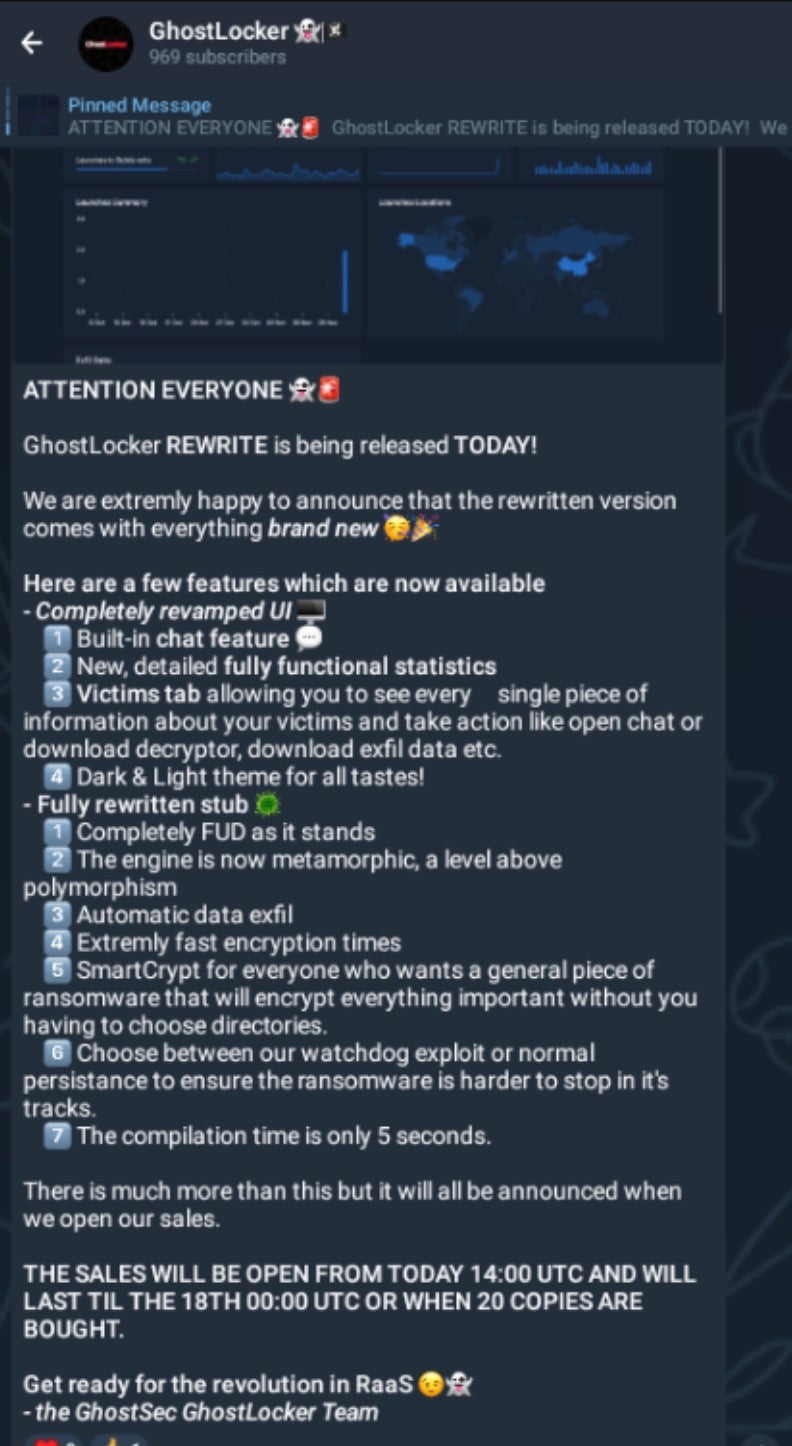
The core features of GhostLocker are quoted to include:
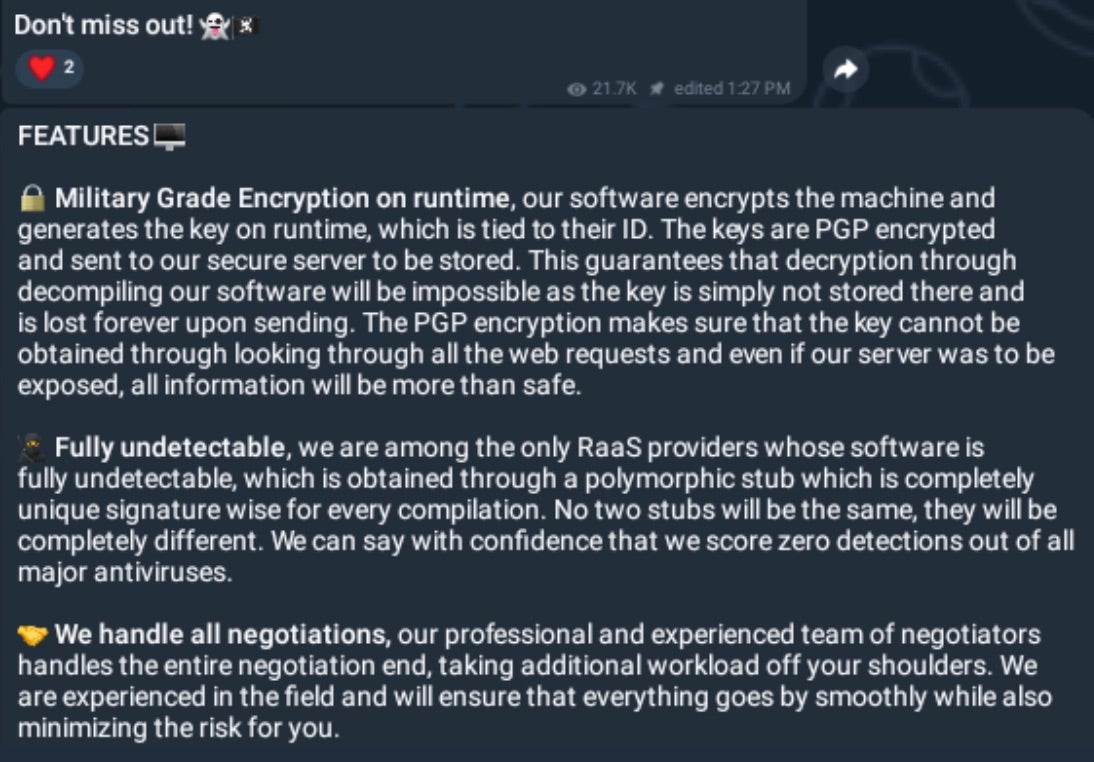
- Military grade encryption on runtime
- Anti Detection (anti-AV/EDR)
- Automated data exfiltration
- Multiple persistence options with “WatchDog” process capabilities
- “Metamorphic” engine
- Extremely fast encryption times
- SmartCrypt for streamlining encryption options
How to Detect GhostLocker RaaS
The SentinelOne Singularity XDR Platform can identify and stop any malicious activities and items related to GhostLocker RaaS.
In case you do not have SentinelOne deployed, detecting GhostLocker RaaS requires a combination of technical and operational measures designed to identify and flag suspicious activity on the network. This allows the organization to take appropriate action, and to prevent or mitigate the impact of the ransomware attack.
To detect GhostLocker RaaS without SentinelOne deployed, it is important to take a multi-layered approach, which includes the following steps:
- Use anti-malware software or other security tools capable of detecting and blocking known ransomware variants. These tools may use signatures, heuristics, or machine learning algorithms, to identify and block suspicious files or activities.
- Monitor network traffic and look for indicators of compromise, such as unusual network traffic patterns or communication with known command-and-control servers.
- Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify network and system vulnerabilities and ensure that all security controls are in place and functioning properly.
- Educate and train employees on cybersecurity best practices, including identifying and reporting suspicious emails or other threats.
- Implement a robust backup and recovery plan to ensure that the organization has a copy of its data and can restore it in case of an attack.
How to Mitigate GhostLocker RaaS
The SentinelOne Singularity XDR Platform can return systems to their original state using either the Quarantine or Repair.
In case you do not have SentinelOne deployed, there are several steps that organizations can take to mitigate the risk of GhostLocker RaaS attacks:
- Educate employees: Employees should be educated on the risks of ransomware, and on how to identify and avoid phishing emails, malicious attachments, and other threats. They should be encouraged to report suspicious emails or attachments, and to avoid opening them, or clicking on links or buttons in them.
- Implement strong passwords: Organizations should implement strong, unique passwords for all user accounts, and should regularly update and rotate these passwords. Passwords should be at least 8 characters long, and should include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Enable multi-factor authentication: Organizations should enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts, to provide an additional layer of security. This can be done through the use of mobile apps, such as Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator, or through the use of physical tokens or smart cards.
- Update and patch systems: Organizations should regularly update and patch their systems, to fix any known vulnerabilities, and to prevent attackers from exploiting them. This includes updating the operating system, applications, and firmware on all devices, as well as disabling any unnecessary or unused services or protocols.
- Implement backup and disaster recovery: Organizations should implement regular backup and disaster recovery (BDR) processes, to ensure that they can recover from ransomware attacks, or other disasters. This includes creating regular backups of all data and systems, and storing these backups in a secure, offsite location. The backups should be tested regularly, to ensure that they are working, and that they can be restored quickly and easily.
GhostLocker Ransomware FAQs
What is GhostLocker ransomware?
GhostLocker is a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) created by GhostSec hacktivist groups. It was launched in October 2023 following collaborative operations with the Stormous ransomware group. GhostLocker 2.0 is a newer strain that exfiltrates and encrypts the victim’s files and demands a ransom for the decryption key. They will lock your files and ask for payment to unlock them.
What industries or regions are most frequently targeted by GhostLocker?
GhostLocker targets multiple sectors, including technology, universities, manufacturing, transportation, and government entities. Its victims can be found across the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. Specific countries impacted include Brazil, India, China, South Africa, Egypt, and Turkey. The company will focus on organisations with valuable data that might pay ransoms quickly.
What programming language is GhostLocker written in?
GhostLocker has two variants with different programming languages. The original GhostLocker 1.0 was written in a Python-based script. The newer GhostLocker 2.0 is written in Go, making it more challenging to analyse and detect. If you examine the code, you’ll find this programming shift represents a significant evolution in the threat.
What encryption algorithms does GhostLocker use?
GhostLocker uses the Fernet symmetric encryption algorithm for key generation. The ransomware generates a Secret key sent to the threat actor via a JSON file. This key is then used while encrypting the files. They will ensure your files are securely locked, making it difficult to recover without the decryption key.
What file extension does GhostLocker append to encrypted files?
Based on the provided search results, no specific information exists about the file extension GhostLocker appends to encrypted files. You should look for unusual file extensions on encrypted files as potential indicators of a GhostLocker infection. If you find strange extensions on multiple files, they will likely be evidence of encryption.
What are the indicators of compromise (IOCs) for GhostLocker ransomware?
IOCs for GhostLocker include connections to C2 servers (one traced to “hxxp[://]41[.]216[.]183[.]31[/]incrementLaunch”), the presence of the ransomware in the Windows Startup folder, and unusual system activities. Affiliates use a control panel tracked in Moscow. These indicators will help identify a potential infection if you check your systems.
How can organisations detect a GhostLocker ransomware infection?
You can detect GhostLocker by monitoring connections to known C2 servers, suspicious activities in the Windows Startup folder, and unusual encryption processes. Watch for random 32-byte ID generation and data exfiltration. You should implement network monitoring tools and update security solutions to catch these activities before full encryption occurs.
What prevention strategies can help block GhostLocker attacks?
You should implement defense-in-depth security measures, update detection signatures regularly, and isolate public-facing systems with DMZs. Make regular backups and keep them offline—Block known IOCs on all security solutions. If you periodically harden applications, databases, servers, and network devices, they will have a more challenging time penetrating your systems.
What should be done immediately after detecting a GhostLocker ransomware attack?
You should immediately isolate infected systems to prevent lateral movement. Disconnect from the network and begin incident response procedures. Report the attack to law enforcement. If you have backups, prepare for restoration. They will try to pressure you with data leaks, so you should assess what information may have been compromised.