LostTrust Ransomware: In-Depth Analysis, Detection, and Mitigation
What Is LostTrust Ransomware?
The LostTrust ransomware operation emerged in September of 2023 as an evolution of MetaEncrypter, which dates back to early 2022. Currently, LostTrust continues to parallel the MetaEncrypter’s multi-extortion model. In late September 2023, a separately-branded LostTrust victim blog was launched.
While there are updated malware payloads to accompany the evolution to LostTrust, they still contain markup and strings from their MetaEncryptor ancestors. Current analysis also shows lineage to the Mindware (aka SFile) ransomware family.

What Does LostTrust Ransomware Target?
LostTrust ransomware operators target multiple industries with little to no discrimination. This includes attacks on healthcare and educational entities.

How Does LostTrust Ransomware Work?
LostTrust postulates that by exposing their victims to their methodologies, they are putting them in a better overall security posture long-term, claiming that they are providing their victims an actual service.
LostTrust ransom notes contain the following quote, which speak to their ‘cause’:
Our team has an extensive background in legal and so called white hat hacking.
However, clients usually considered the found vulnerabilities to be minor and poorly paid for our services.
So we decided to change our business model. Now you understand how important it is to allocate a good budget for IT security.
This is serious business for us and we really don't want to ruin your privacy, reputation and a company.
We just want to get paid for our work whist finding vulnerabilities in various networks.
LostTrust ransomware payloads will attempt to discover and terminate a plethora of services and processes. Critical services associated with the likes of Microsoft Exchange, MSSQL, SharePoint, Tomcat, postgresql, and more are terminated if identified. This is to ensure that nothing inhibits the encryption and potential exfiltration process. The ransomware initiates numerous hidden CMD.EXE sessions to carry out these tasks.
The hidden CMD.EXE windows subsequently host the observed WMIC, NET, SC, taskkill, VSSADMIN, and wevtutil commands. In addition to process discovery and termination, the ransomware will attempt to remote Volume Shadow Copies (VSS) via VSSADMIN as well as clearing out all Windows Event Logs via WEVTUTIL.EXE. LostTrust ransomware payloads support multiple command-line arguments.
Commands supported by LostTrust ransomware include:
| Argument | Function |
| –enable-shares | Enable discovery and encryption of accessible network volumes |
| –onlypath | Only encrypt files in the specified path |
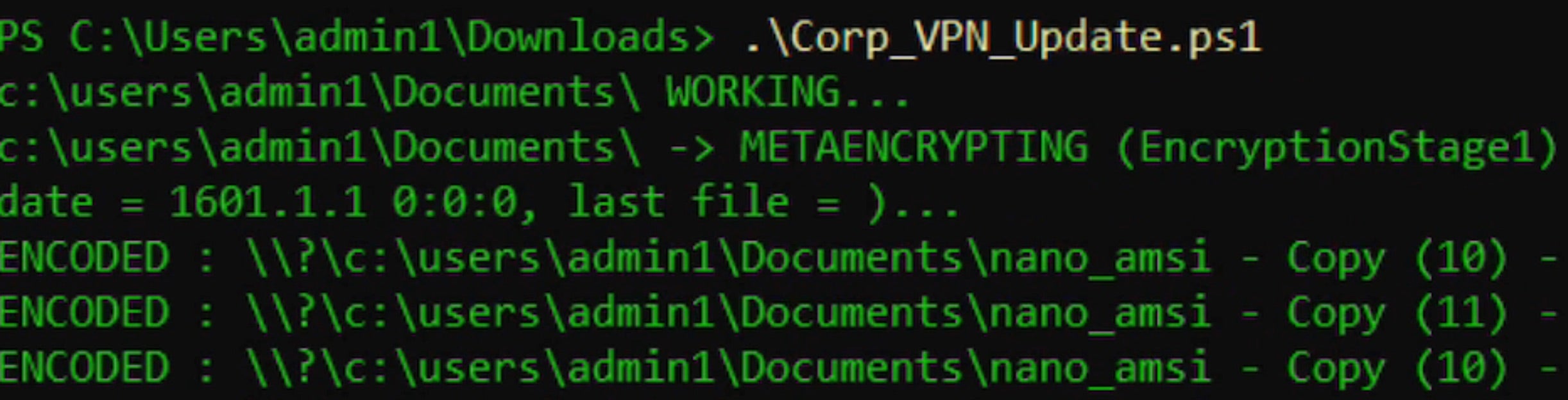
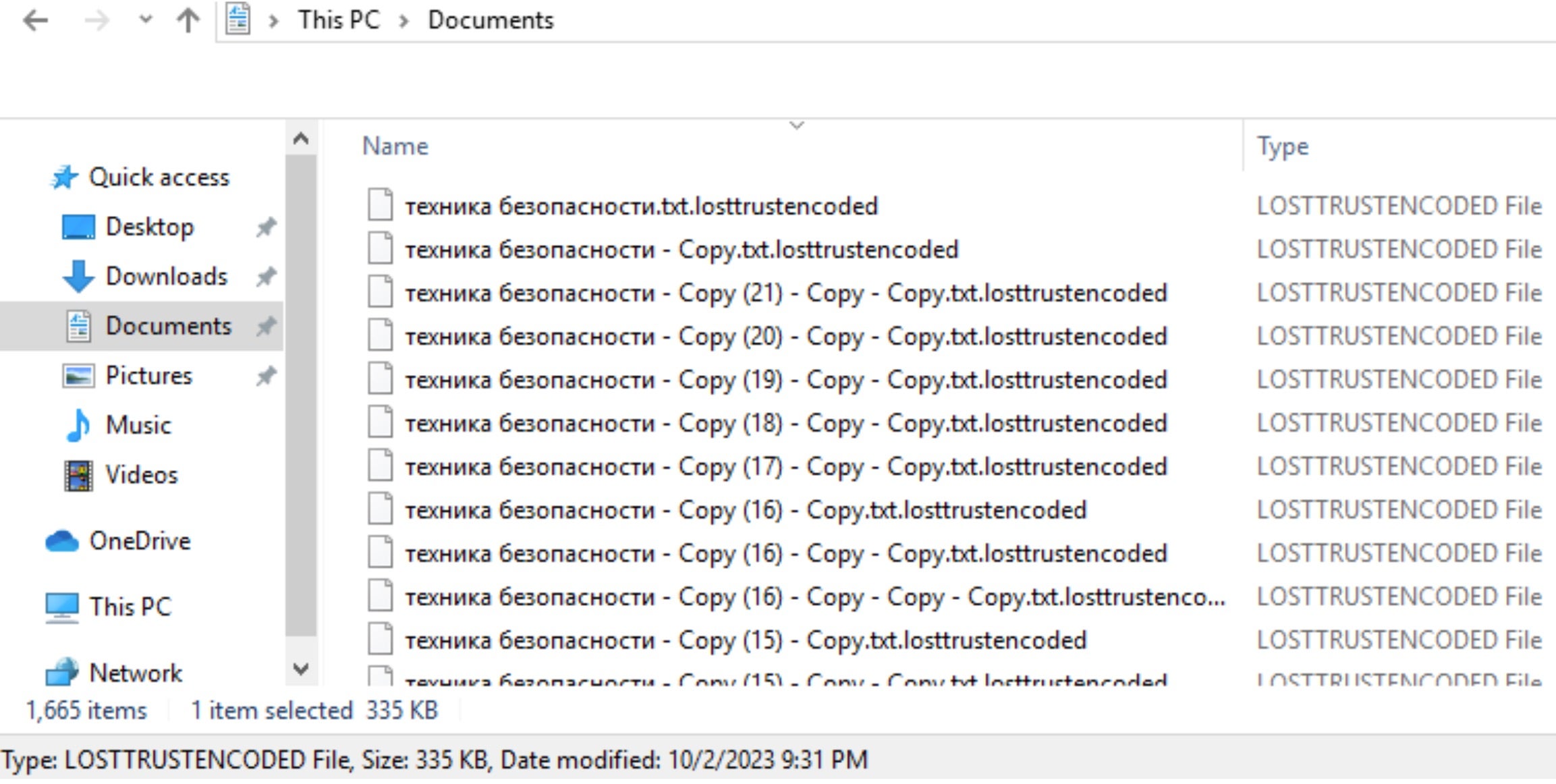
Encrypted files are modified with the “.losttrustencoded” file extension.
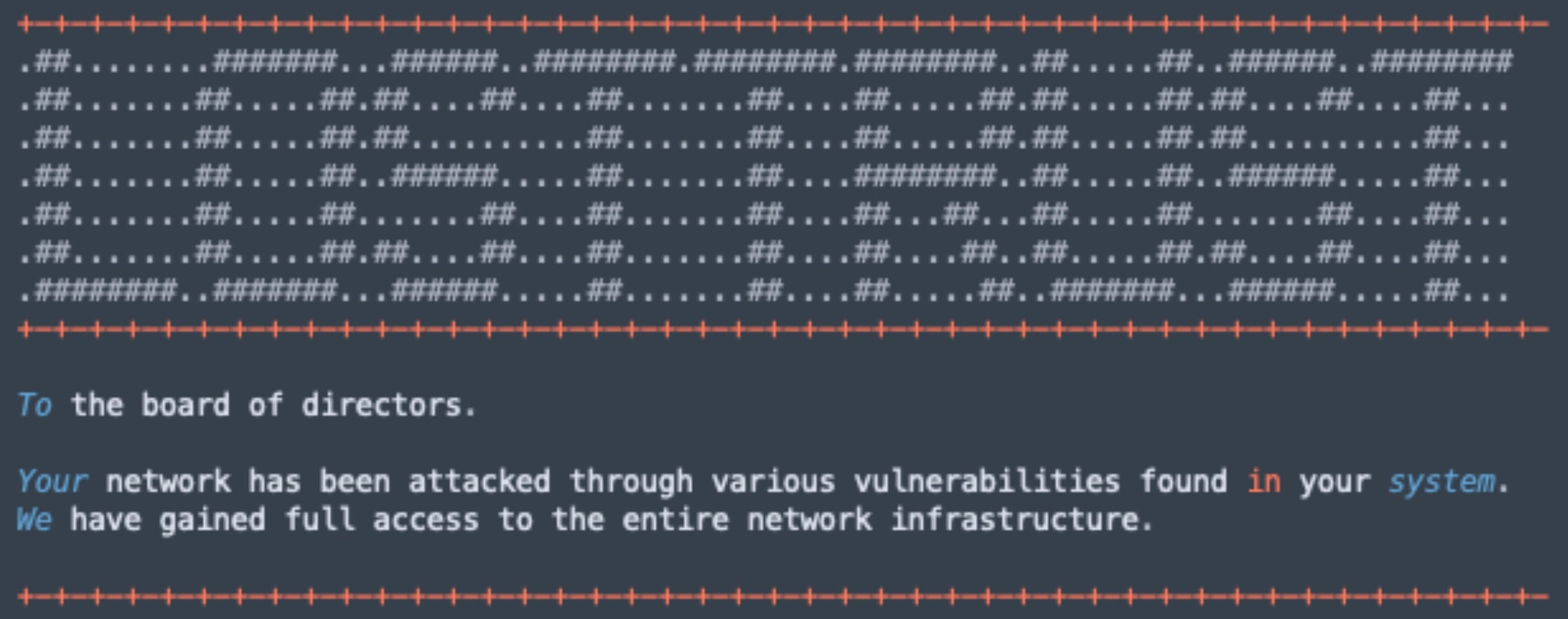
LostTrust ransom notes are written to each folder containing encrypted items as “!!LostTrustEncoded.txt”.
How to Detect LostTrust Ransomware
The SentinelOne Singularity XDR Platform can identify and stop any malicious activities and items related to LostTrust ransomware.
In case you do not have SentinelOne deployed, detecting LostTrust ransomware requires a combination of technical and operational measures designed to identify and flag suspicious activity on the network. This allows the organization to take appropriate action, and to prevent or mitigate the impact of the ransomware attack.
To detect LostTrust ransomware without SentinelOne deployed, it is important to take a multi-layered approach, which includes the following steps:
- Use anti-malware software or other security tools capable of detecting and blocking known ransomware variants. These tools may use signatures, heuristics, or machine learning algorithms, to identify and block suspicious files or activities.
- Monitor network traffic and look for indicators of compromise, such as unusual network traffic patterns or communication with known command-and-control servers.
- Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify network and system vulnerabilities and ensure that all security controls are in place and functioning properly.
- Educate and train employees on cybersecurity best practices, including identifying and reporting suspicious emails or other threats.
- Implement a robust backup and recovery plan to ensure that the organization has a copy of its data and can restore it in case of an attack.
How to Mitigate LostTrust Ransomware
The SentinelOne Singularity XDR Platform can return systems to their original state using either the Quarantine or Repair.
In case you do not have SentinelOne deployed, there are several steps that organizations can take to mitigate the risk of LostTrust ransomware attacks:
- Educate employees: Employees should be educated on the risks of ransomware, and on how to identify and avoid phishing emails, malicious attachments, and other threats. They should be encouraged to report suspicious emails or attachments, and to avoid opening them, or clicking on links or buttons in them.
- Implement strong passwords: Organizations should implement strong, unique passwords for all user accounts, and should regularly update and rotate these passwords. Passwords should be at least 8 characters long, and should include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Enable multi-factor authentication: Organizations should enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts, to provide an additional layer of security. This can be done through the use of mobile apps, such as Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator, or through the use of physical tokens or smart cards.
- Update and patch systems: Organizations should regularly update and patch their systems, to fix any known vulnerabilities, and to prevent attackers from exploiting them. This includes updating the operating system, applications, and firmware on all devices, as well as disabling any unnecessary or unused services or protocols.
- Implement backup and disaster recovery: Organizations should implement regular backup and disaster recovery (BDR) processes, to ensure that they can recover from ransomware attacks, or other disasters. This includes creating regular backups of all data and systems, and storing these backups in a secure, offsite location. The backups should be tested regularly, to ensure that they are working, and that they can be restored quickly and easily.
LostTrust Ransomware FAQs
What is LostTrust ransomware?
LostTrust is a file-encrypting malware that locks your essential data and demands payment for decryption. It was first discovered in early 2023. When LostTrust infects your system, it scans for valuable files and encrypts them. You will see a ransom note titled recover-files.txt on your desktop. The attackers will provide instructions on contacting them through a Tor website and paying the ransom in cryptocurrency.
What platforms does LostTrust ransomware target?
LostTrust primarily targets Windows operating systems, from Windows 7 to Windows 11. It will also attack Windows Server environments. The ransomware can infect Linux servers in some cases. You should be especially careful if you run older, unpatched versions of these systems. They will attempt to exploit known vulnerabilities in these platforms to gain access and deploy their malicious payloads.
What encryption methods does LostTrust ransomware use?
LostTrust uses a combination of AES-256 for file encryption and RSA-2048 for key encryption. They will generate unique encryption keys for each victim. Your files are encrypted with the AES key, which is then encrypted with the RSA public key. The private decryption key is kept on the attackers’ servers, making it nearly impossible to decrypt files without paying the ransom.
What file extension does LostTrust append to encrypted files?
LostTrust appends the .lostrust extension to all encrypted files. For example, “document.docx” becomes “document.docx.lostrust” after encryption. They will also change file icons to a custom red lock symbol. You can quickly identify affected files with this extension. The ransomware will encrypt almost all common file types, including documents, images, databases, and backups.
What are the indicators of compromise (IOCs) for LostTrust ransomware?
LostTrust IOCs include unusual network traffic to suspicious IP addresses. You can spot .lostrust file extensions and ransom notes named recover-files.txt. There are suspicious registry modifications that persist across reboots. The ransomware will create scheduled tasks with random names. You should also look for disabled security services and new user accounts with admin privileges.
How can organisations detect a LostTrust ransomware infection?
You can detect LostTrust by monitoring for mass file modifications and high disk activity. There are suspicious event logs showing security service termination. You should watch for unexpected network scanning. The ransomware will generate alerts about credential theft attempts. You’re likely infected if you see PowerShell executing encoded commands or unusual outbound connections to Tor networks.
What security measures help prevent LostTrust ransomware attacks?
You should implement multi-factor authentication on all remote access services. Email security gateways can block phishing attempts. Regularly patching and updating systems reduces vulnerability. Segmenting your network limits lateral movement. The best defense includes regular offline backups, employee security training, and application allow listing to block unauthorised executables from running on your systems.
Can endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools stop LostTrust ransomware?
Yes, good EDR solutions can detect and block LostTrust ransomware behaviors and monitor for suspicious file encryption patterns. You should deploy solutions that offer real-time protection. The EDR tools can identify malicious PowerShell scripts and unusual process behaviors. Implementing proper EDR configuration will help prevent initial access and stop the encryption before it spreads across your network.
What techniques does LostTrust use for lateral movement within a network?
LostTrust uses credential harvesting tools like Mimikatz to steal passwords. It exploits SMB shares to spread across networks. You should watch for unusual PowerShell commands and remote process creation. The ransomware uses legitimate tools like PsExec and WMI to move. It connects to domain controllers to gather account information and uses stolen admin credentials to access other systems.
Does LostTrust ransomware exfiltrate data before encryption?
Yes, LostTrust employs double extortion tactics by stealing your data before encryption. They will exfiltrate sensitive information to their servers. If you don’t pay, you face threats of data publication. The attackers will take screenshots, steal credentials, and gather business documents. This data theft typically occurs 1-3 days before the encryption begins, giving them leverage for higher ransom demands.