In this blog post, we delve into the notable trends that have been shaping the cyber landscape over the past month. Several high profile threat operators have continued to briefly disappear only to re-emerge, lending to a more dynamic ransomware landscape. Highlighting the risks seen in the identity attack surface, we also continue to see the fallout from this season’s onslaught of attacks against Identity Access Management (IAM) platforms, specifically. Finally, this post discusses new cyber initiatives and counter-operations from the federal government to support global collaboration across the cyber threat environment and recent law enforcement wins.

Emerging Pressure Tactics In Ransomware Schemes
In the latest ransomware and extortion operations, financially motivated actors are leveraging new ways to pressure their victims into complying to their demands. Groups like ALPHV, for example, are now openly threatening to report victims to the SEC for violation of public disclosure for breaches they themselves committed. We have also observed groups like Rhysida threatening to expose illicit and incriminating data that was discovered upon exfiltration of the victim data.
Recent developments in legal frameworks, including the SEC’s updated rules for cybersecurity incident reporting, GDPR, and existing data protection laws, are being manipulated to increase pressure on organizations that are already at risk. Cybercriminals are using these regulations to heighten victims’ fears of legal repercussions and damage to their reputation, thereby forcing them into paying ransoms.
This trend highlights the urgency for organizations to bolster their cybersecurity measures, adhere to regulatory standards, and stay prepared for the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats. With cybercriminals constantly seeking innovative methods to exploit businesses, it is important for cyberdefense teams to maintain vigilance and adaptability in their approaches to counter these advancing threats.
A previous blog post we published discusses the increasing “leveling up” of pressure tactics coupled with troubling victimology, painting a potentially problematic picture of how attacks are likely to play out in the near future. Companies dealing with this multi-pronged extortion onslaught include the likes of Toyota, Delta Dental, Fred Hutch Cancer Center, Kraft Foods, Idaho National Lab and more. There is more potential damage being done now in the big-game ransomware operation attacks and the frequency of these attacks deserves much consideration.
Multi-looting is amongst the tactics leveraged by these modern more extensive options—one example of this emerging behavior developed between ALPHV and medical product manufacturer, Henry Schein. According to reports, this victim experienced multiple encryptions during recovery and negotiation.
On Again, Off Again | Fluctuations In Ransomware Groups
As of this writing, the FBI has officially confirmed their seizure of the primary BlackCat/ALPHV infrastructure. The TOR sites have been seized and victims are now able to obtain decryption tools from the FBI via an IC3 filing. Victims of BlackCat ransomware are strongly encouraged to contact their FBI field office for further information and to determine next steps and options for assistance.

This is a sizeable victory indeed, as per the FBI’s notice: “Blackcat actors have compromised computer networks in the United States and worldwide. The disruptions caused by the ransomware variant have affected U.S. critical infrastructure – including government facilities, emergency services, defense industrial base companies, critical manufacturing, and healthcare and public health facilities – as well as other corporations, government entities, and schools. The loss amount globally is in the hundreds of millions and includes ransom payments, destruction and theft of proprietary data, and costs associated with incident response.”
Within a similar timeframe, NoEscape also appeared to have closed up shop whilst holding onto millions of dollars in funds due to their affiliates. This is known as an exit scam, and the primary operators of NoEscape appear to have ceased communicating with both their partners and affiliates. There are a number of arbitration complaints against the operators on various major crimeware forums. These same forums and dark markets appear to have banned the operators from further activity in those forums.
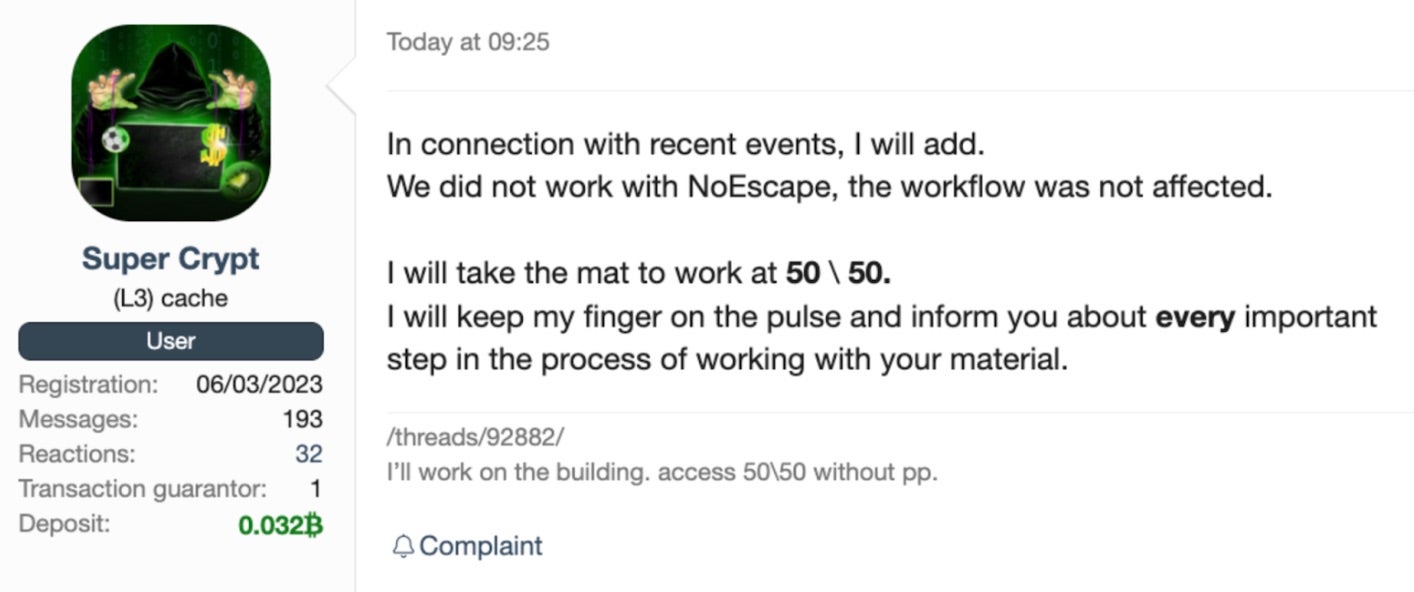
Adding to the already foggy situation, LockBit ransomware operations are reportedly attempting to recruit affiliates directly from the potential pool of those that have been “done wrong” by NoEscape and ALPHV operations.
A Year End Rise In Identity-Focused Attacks
Identity compromise, and the subsequent use of valid credentials to perform illegitimate activities, is nearly ubiquitous in the modern landscape of cyberattacks. IAM platforms play a crucial role in both enhancing security and improving user experience by streamlining access processes within an organization. They are particularly important in large and medium-sized businesses where managing a large number of user identities and permissions is a complex task.
The compromise of market-leading IAM platforms continues to blossom and expand as we head towards the end of 2023. When we discuss the compromises of enterprises like 1Password, LastPass, BeyondTrust, and other identity management providers, the thing to keep in mind is the long-term and downstream effects. Outside of the immediate problem of compromised credentials and accounts, victims also face the ongoing issues associated with associated legal issues that may arise, damaged reputation, and associated loss of revenue. Also to consider is that, once compromised, it is trivial for the attacker to leverage the platform to start intercepting the data and traffic belonging to platform users. In this scenario, a single compromise of an IAM extends to many victim environments.
The consequences of a security breach in an IAM platform are far-reaching and can impact an organization on multiple fronts, including financial, legal, operational, and reputational aspects. It underscores the critical importance of robust security measures and constant vigilance in managing these systems. The downstream effects of breaches within the likes of 1Password, LastPass, and similar will be felt going into 2024 and beyond.
Forum and Dark Market Updates
We previously discussed ongoing cyber activity occurring on Telegram in our September cybercrime update. In the context of low-sophistication cybercrime marketing and sales, Telegram has collected a reputation for being a “Wild Wild West-like” hub for criminal activities. Accounts, proxy access, mail/identity lists and data, VPS services, FUD crypting, bank logs, and SIM/cell carrier services (aka SIM-swapping) are all available with essentially zero barrier to entry. Cybercrime actors of all types continue to congregate within relevant Telegram channels.
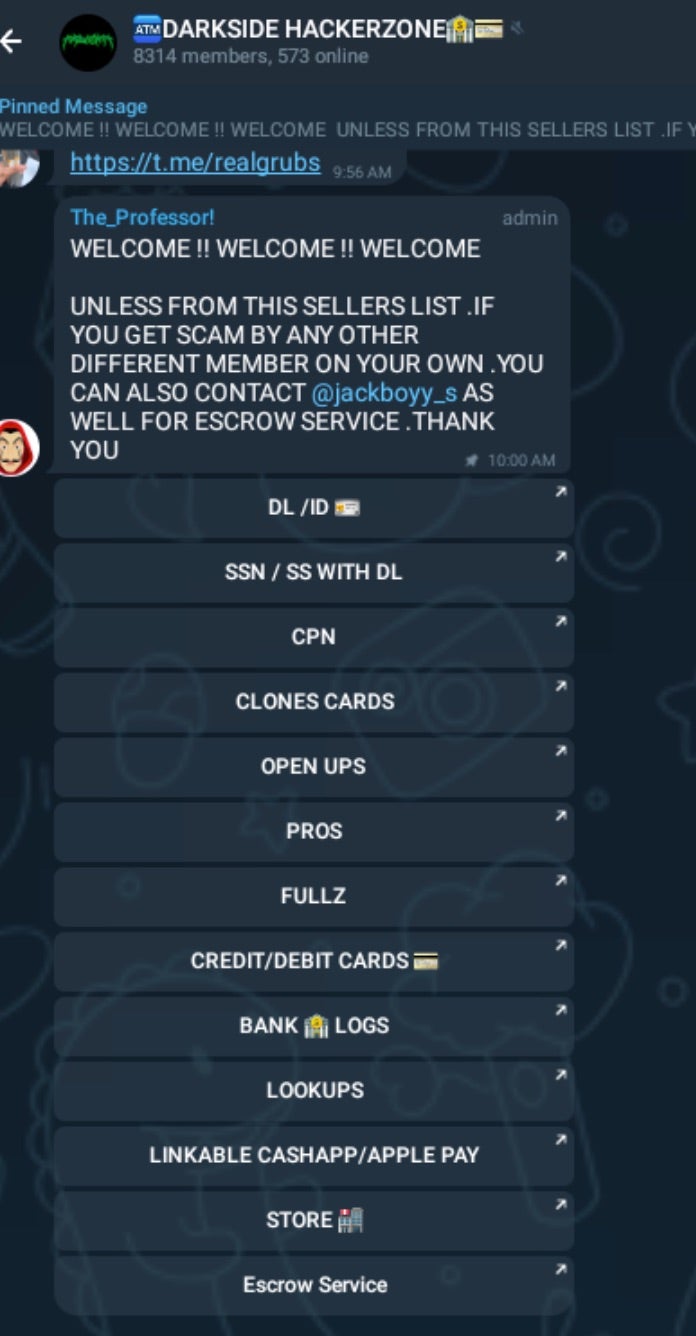
Given the approaching holiday season, we are seeing many channels and bots providing pseudo-sales and promotions on malware kits, tools, and other illicit services.
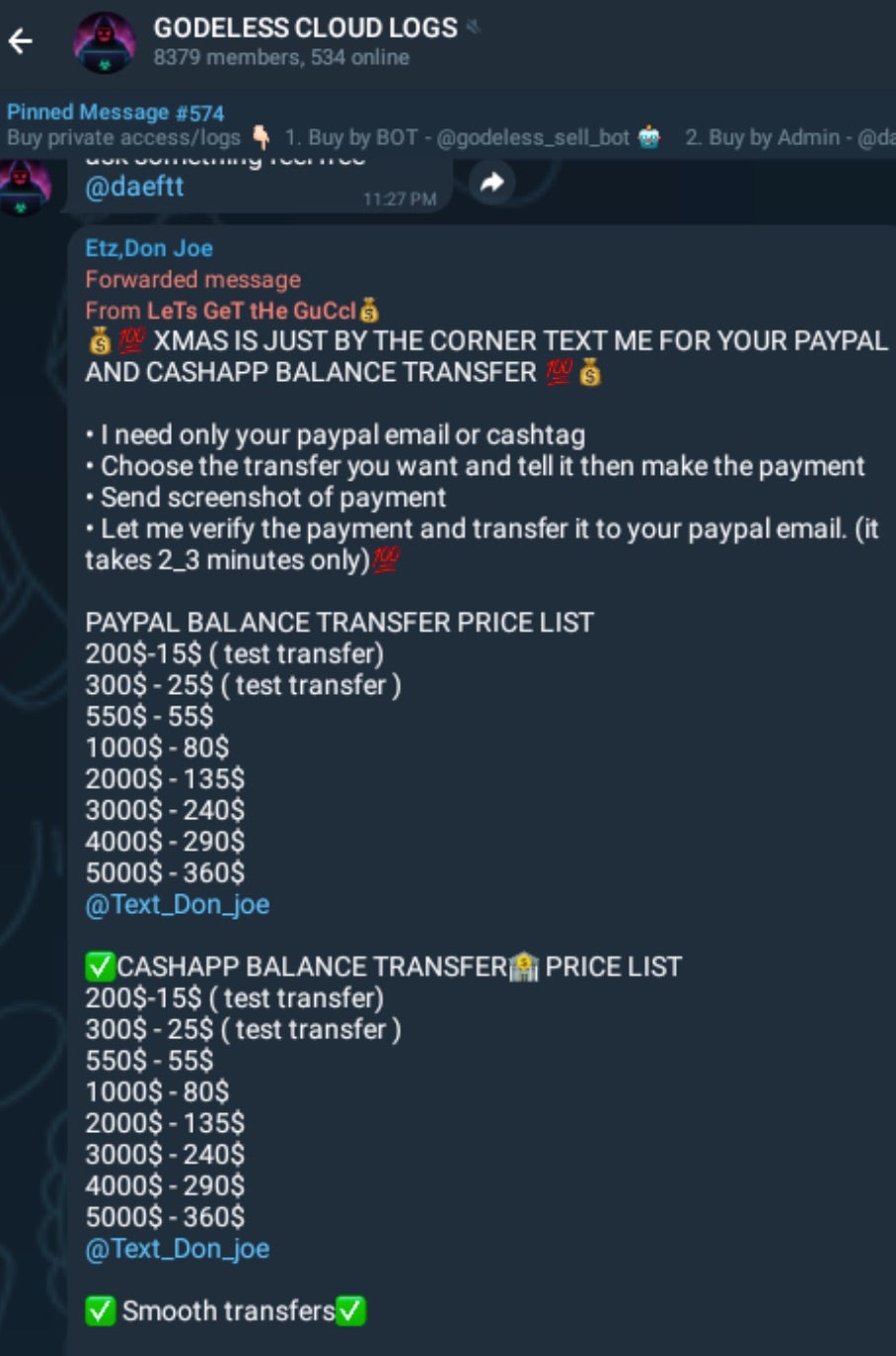
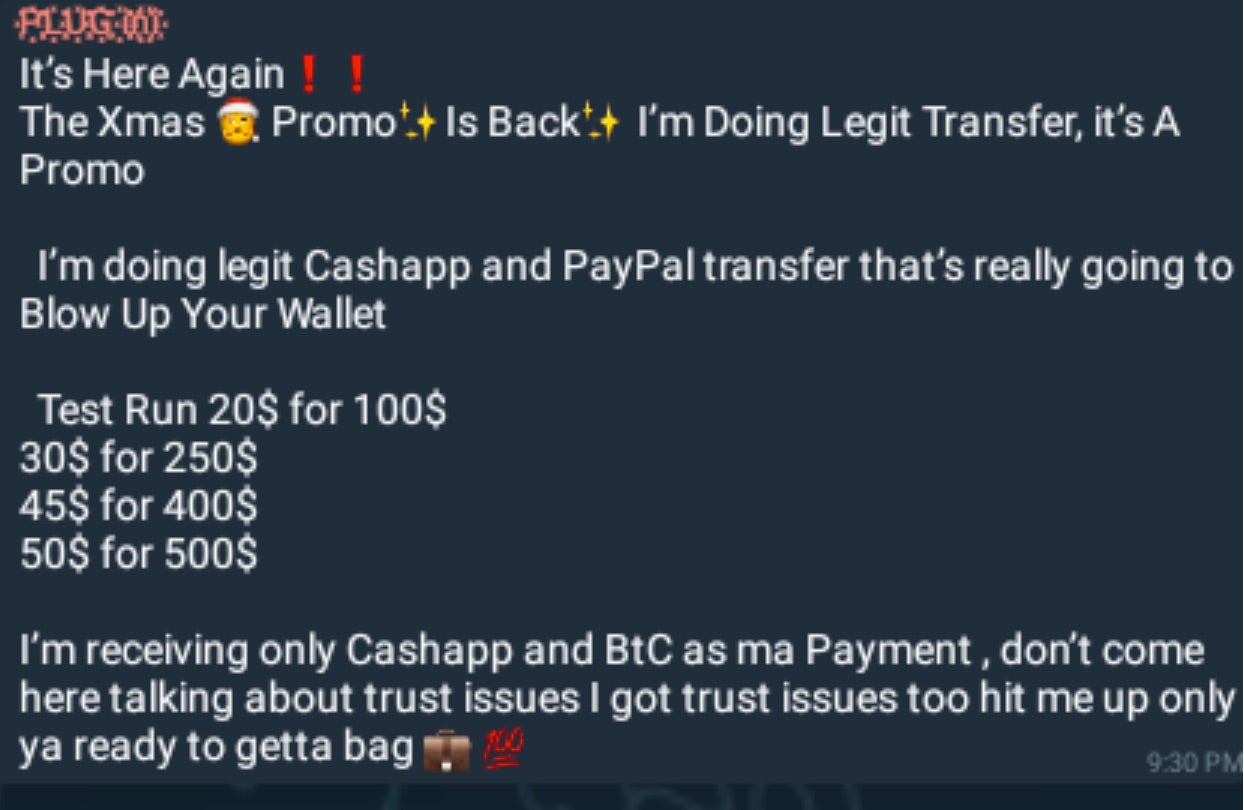
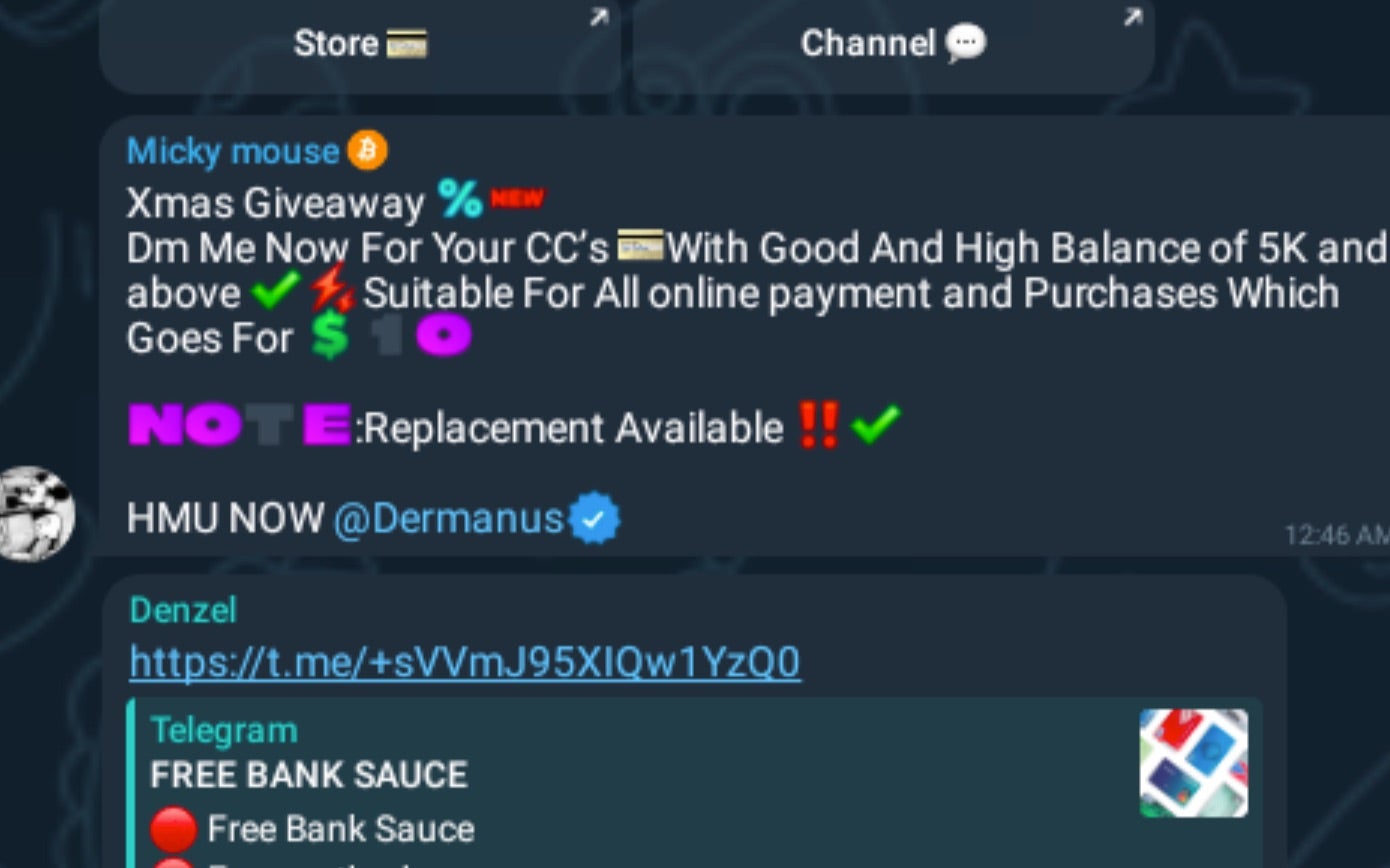
On the subject of forums, the Clearnet forum launched by Cyber Drag0nz in September appears to now be down or defunct. In a broader trend, it seems that many of the smaller Middle-Eastern crimeware operations, which have been amplified with the onset of the Israel-Hamas war, are showing their true size and abilities.
New Initiatives and Counter-Operations
In the final month of 2023, the information security community has seen more law enforcement activities such as crackdowns and arrests in parallel with some new and positive developments from the recent Counter Ransomware Initiative (CRI) Summit.
At the tail end of November, a large-scale option out of Europol led to the arrests of numerous ransomware affiliate actors associated with LockerGoga, MegaCortex, Hive, and Dharma. This action follows the initial wave of arrests that occurred in 2021. The recent action was focused across regions in Ukraine. Considered a large victory for global law enforcement agencies, these takedowns go some considerable distance in chipping away at the infrastructure of known threat actor infrastructure.
Notably, we also saw the arrest of an alleged ringleader of the Kelvin Security hacking group this past month in Spain. The detainee was a primary figure in an associated money laundering activity which focused on cryptocurrency exchanges. This is an especially satisfying victory for law enforcement given the scope of the involved victimology. According to the released statements, the group has operated since 2013 and has carried out more than 300 high-level cyberattacks in the last three years, targeting strategic industries in over 90 countries, including the U.S., Germany, Italy, Argentina, Chile, and Japan.
Along those lines, an individual known as FFX pleaded guilty to charges surrounding their involvement in the development of Trickbot malware. Specifically, the Russian national was known for their contributions to the malware’s browser injection components, along with mechanisms for deployment and management of additional code (e.g., ransomware payloads). The developer currently faces a maximum sentence of 35 years in prison for charges related to computer fraud, identity theft, wire, and bank fraud.
Recent developments from the highest levels of government are set to shape upcoming cybersecurity initiatives in the new year. At the latest Counter Ransomware Initiative Summit, members from across the world focused on global collaboration in ongoing cybersecurity strategies. Representatives from 50 countries discussed new methods to combat ransomware threats. Key topics included strengthening international cooperation, tackling financial underpinnings of ransomware, and enhancing public-private partnerships. The summit highlighted the evolving role of AI in cybersecurity and emphasized the importance of information sharing and policy initiatives to disrupt ransomware financing. These efforts aim to build a more resilient global cybersecurity infrastructure against the growing threat of ransomware.
Conclusion
After examining the past month, several compelling trends continue to demand our attention. High-profile threat operators, momentarily vanishing only to resurface later, have rendered the ransomware landscape more dynamic than ever. Ongoing attacks on leading IAM platforms signal to security leaders the very real vulnerabilities linked to the identity surface. Cybercriminals are shifting towards new methods in pressuring their victims to pay exuberant ransoms.
In the wake of these challenges, new cyber initiatives and counter-operations spearheaded by international federal governments are in place to address and push innovation in incident response, threat intel sharing, and other preventative measures.
In the face of these emerging trends, employing a comprehensive security solution like SentinelOne’s Singularity XDR, which leverages AI and automated remediation, can serve as a potent weapon in an organization’s cybersecurity arsenal. It’s more crucial than ever to stay ahead of the curve, adopting proactive measures that help detect and mitigate threats before they can inflict significant damage.
To learn more about how SentinelOne can help defend your organization’s endpoint, cloud, and network assets, contact us or request a free demo.