Current and emerging cyber threats continue to show global enterprises why traditional security measures are no longer adequate defenses. To help enterprises pave a clearer path forward in building cyber resilience, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) recently released its Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM).
The ZTMM provides a framework for business in all industries as they implement zero trust policies into their day-to-day operations and overarching security strategies. Zero trust has rapidly become an essential element in crafting a strong security posture capable of staving off modern adversaries.
In this post, we explore the key elements of CISA’s recommendations for zero trust and how SentineOne’s AI-powered XDR platform empowers enterprises to meet the challenge of embracing zero trust in today’s digital landscape.

Understanding CISA’s Approach to Implementing Zero Trust
CISA’s ZTMM provides guidance in the development of effective and actionable zero trust strategies and solutions. Their approach to zero trust revolves around the reduction of cyber risk, increasing speed and agility to stay paces ahead of adversaries, and improving enterprises’ overall security defenses and resilience.
The premise of zero trust adheres to a strategy where no user or asset is to be implicitly trusted in an environment. This involves adopting an ‘assume breach’ mentality and works by making continuous verification of each user, device, and application mandatory. Zero trust as a whole requires enterprises to evolve their greater security philosophy, culture, and policies.
While the ZTMM is specifically tailored for federal agencies, businesses in all verticals can benefit from these recommendations and use them to safeguard against industry-specific risks.
What Are the Five Pillars of ZTMM?
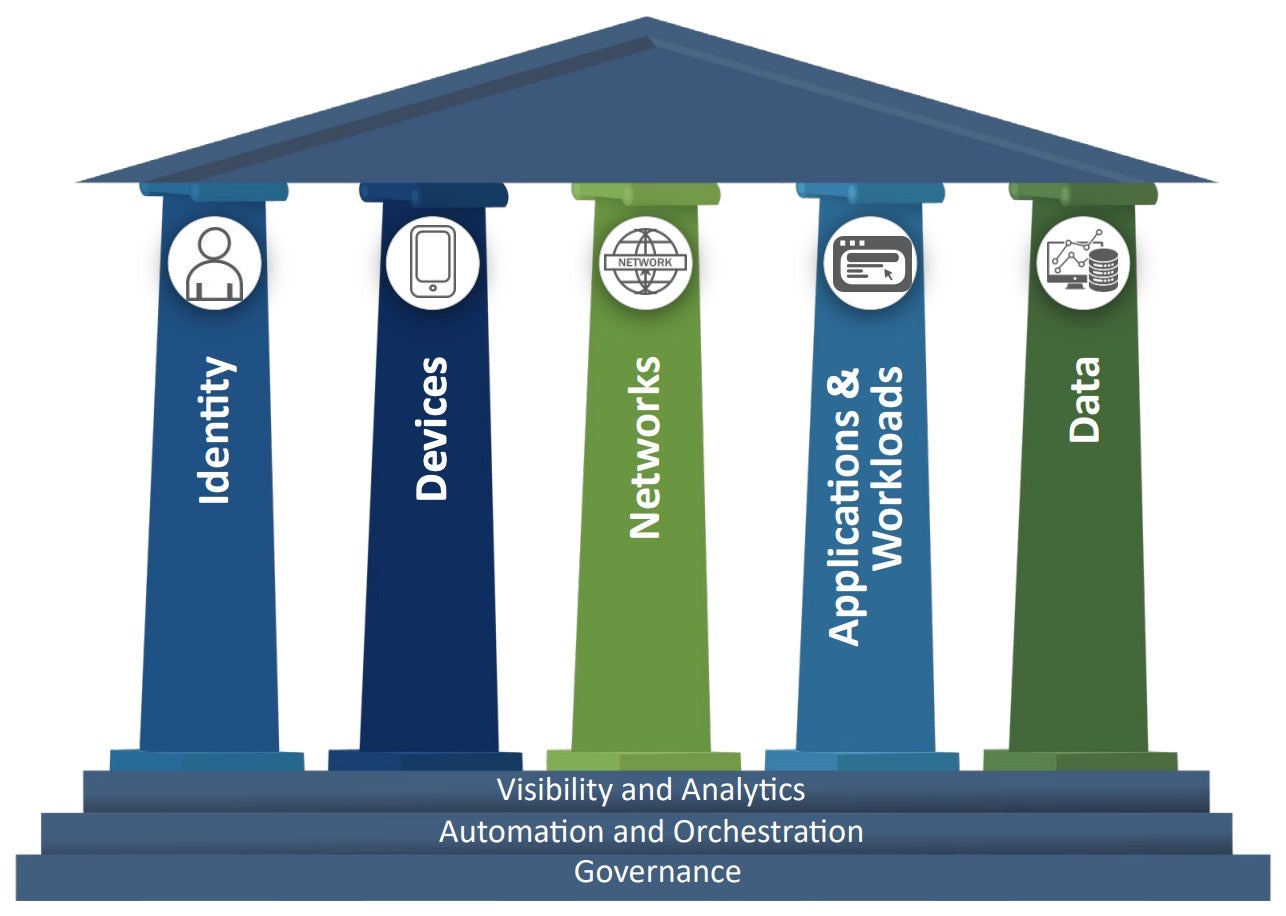
CISA’s ZTMM is comprised of five main pillars: Identity, Devices, Networks, Applications and Workloads, and Data.
- Identity – This pillar focuses on authenticating and authorizing users and devices before granting access to resources. It involves creating a unified identity and access management (IAM) system and implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users.
- Devices – This pillar focuses on securing all IoT devices that connect to an organization’s network. It involves creating a comprehensive inventory of all devices and implementing endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
- Networks – This pillar focuses on securing all network traffic, regardless of the user’s location or resource. It involves implementing network segmentation and micro-segmentation to limit resource access and use secure communication protocols such as Transport Layer Security (TLS).
- Applications and Workloads – This pillar focuses on securing all applications and workloads, whether they’re hosted on-premises or in the cloud. It involves implementing application-level access controls and using secure coding practices to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Data – This pillar focuses on securing all data, whether it is at rest or in transit. It involves implementing encryption and access controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Essential Capabilities for Effective Zero Trust
In CISA’s zero trust framework, three cross-cutting capabilities can be used by enterprises on their journey to adopting zero trust: Visibility and Analytics, Automation and Orchestration, and Governance. These capabilities support the interoperability of functions across the pillars.
- Visibility and Analytics – Focusing on data analysis allows enterprises to better inform policy decisions, action response activities, and build out risk profiles so security teams can proactively take measures before incidents occur.
- Automation and Orchestration – In a zero trust model, automated tools and workflows support security response functions while maintaining oversight, security, and interaction of the development process for such functions, products, and services.
- Governance – This refers to the definition and enforcement of cybersecurity policies, procedures, and processes. Senior leadership in an enterprise holds accountability in managing and mitigating security risks in support of zero trust principles from the top down.
Implementing these pillars can be a complex process requiring significant organizational planning and coordination. However, the benefits of implementing zero trust are substantial, improving security posture, reducing risk of data breaches, and increasing visibility into network activity.
How SentinelOne Supports Successful Zero Trust Adoption
Implementing zero trust requires a comprehensive approach that covers all aspects of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Enterprises worldwide trust the SentinelOne platform to enable their ongoing journey in adopting zero trust policies that work for their businesses.
The SentinelOne platform helps streamline and action many of the recommendations from CISA’s ZTMM by extending visibility, analytics, and response capabilities across endpoint, identity, cloud, and network surfaces.
Identity Pillar | Advanced Identity Protection & Threat Response
SentinelOne provides comprehensive identity security capabilities, including identity risk reduction, threat detection and response, and identity deception. Going a step further than traditional IAM, SentinelOne’s identity protection solution proactively reduces the identity infrastructure attack surface by closing gaps in commonly exploited Active Directory and Azure AD environments and thwarting attack progress through misdirection tactics.
Devices Pillar | Autonomous Prevention, Detection & Response
SentinelOne’s EDR capabilities provide real-time visibility into endpoint activity, allowing organizations to detect and respond to threats rapidly. Since endpoints remain a key attack vector for threat actors, SentinelOne combines static and behavioral detections to neutralize known and unknown threats.
Networks Pillar | Powerful Network Detection Response & Micro-Segmentation
Lack of visibility due to legacy network controls breeds gaps and inconsistencies that threat actors can exploit. SentinelOne’s platform gives enterprises full visibility and control of their network, allowing security teams to monitor and isolate compromised devices and stop lateral movement. SentinelOne agents also create detailed network topology to support forensic investigations, decision making processes, and micro-segmentation policy creation.
Applications & Workloads Pillar | Complete Runtime Control & Workload Protection
Cloud computing and hybrid workspaces are commonplace now for the worlds’ businesses. As cloud-based attacks rise in number and complexity, SentinelOne combats threats on this attack surface by providing application-level access controls and uses secure coding practices to prevent vulnerabilities. Businesses can manage and secure hybrid, private, and multi-cloud workloads from a single console with a single agent.
Data Pillar | Shifting Away From Perimeter-Based Security
In the past, enterprises stored sensitive data behind their corporate networks. As more make the move over to cloud applications, simply defending the perimeter against external threats is not enough. SentinelOne’s platform provides encryption and access controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data from the inside out.
Conclusion
The zero trust philosophy presents a shift from a location-centric model to an identity, context, and data-centric approach with fine-grained security controls between users, systems, applications, data, and assets that change over time. In CISA’s latest Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM), enterprises are reminded of the “never trust, always verify” tenet that protects environments from both external and internal cyber threats.
As steady transformation in remote work policies and the rise of cloud adoption present new challenges for security defenders, SentinelOne is committed to helping enterprises implement zero trust architectures effectively. The Singularity platform is designed to provide comprehensive visibility and control over all endpoints, users, and networks in a single agent, allowing security teams to achieve optimal zero trust elements across all pillars of the ZTMM.
If you’re interested in learning more about how SentinelOne can help your business achieve the ideal level of zero trust maturity, contact us today or book a demo here.